Caulimoviridae (taxid:186534)
VIRION
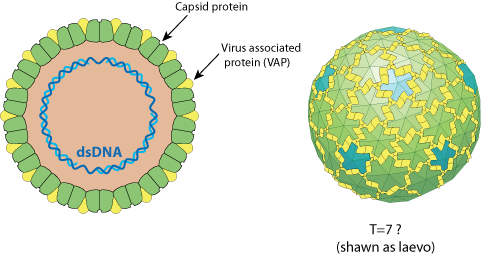
Virions not enveloped, bacilliform (30 x 60-900 nm) or isometric (45-50 nm in diameter).
GENOME
Monopartite, open circular, double stranded DNA of 7000-8200 base pairs with discontinuities in both strands: one in the transcribed strand and one to three in the non-transcribed strand. Encode for 1 to 8 proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
The genome encodes a genomic mRNA, which may be alternatively spliced in some genera. The genomic mRNA generally encodes multiple ORFs expressed by ribosomal shunt.
ENZYMES
- Reverse transcriptase
- RNAse H [RT]
- Polyprotein protease (Peptidase A3) [PRO]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC / NUCLEAR
- Attachment of viral proteins to host receptors mediates entry into the host cell.
- The viral dsDNA is released into the nucleus.
- Transcribed by host RNA polymerase II.
- mRNA translation produces viral proteins.
- Genomic RNA is retrotranscribed into new dsDNA genomes in the cytoplasm.
- Genomes are encapsidated by the capsid protein and form new virions.
- The virion infects either a new cell by plasmodesmata movement, or by insect vector uptake.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)79 entries grouped by strain
9 entries
Soybean chlorotic mottle virus reference strain
7 entries
Cestrum yellow leaf curling virus (CmYLCV) reference strain
6 entries
Carnation etched ring virus (CERV) reference strain
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain Strasbourg) (CaMV) reference strain
6 entries
Figwort mosaic virus (strain DxS) (FMV) reference strain
5 entries
Cassava vein mosaic virus (CsVMV) reference strain
4 entries
Rice tungro bacilliform virus (isolate Philippines) (RTBV) reference strain
3 entries
Commelina yellow mottle virus (CoYMV) reference strain
1 entry
Petunia vein clearing virus (isolate Shepherd) (PVCV) reference strain
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain BBC) (CaMV)
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain CM-1841) (CaMV)
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain D/H) (CaMV)
6 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain NY8153) (CaMV)
2 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain PV147) (CaMV)
2 entries
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain W260) (CaMV)
1 entry
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain Bari 1) (CaMV)
1 entry
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain D4) (CaMV)
1 entry
Cauliflower mosaic virus (strain S-Japan) (CaMV)
1 entry
Petunia vein clearing virus (isolate Hohn) (PVCV)
Atractylodes mild mottle virus taxid:1711685
Badnavirus maculakalanchoes taxid:3051985
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-03110 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-06000 |
Banana streak CA virus taxid:1016852
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-03113 |
| Virion associated protein | ma-jd-viral-05994 |
Banana streak GF virus taxid:328670
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ORF1 | ma-jd-viral-03118 |
| ORFII | ma-jd-viral-05991 |
Banana streak IM virus taxid:1016853
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-03117 |
| Virion-associated protein | ma-jd-viral-05998 |
Banana streak MY virus taxid:1476909
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ORF I protein | ma-jd-viral-03120 |
| ORF II (Virion associated protein) | ma-jd-viral-05999 |
Banana streak UA virus taxid:1016854
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| P24 | ma-jd-viral-03119 |
| Virion associated protein | ma-jd-viral-54427 |
Banana streak UI virus taxid:1016855
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-03106 |
| Virion associated protein | ma-jd-viral-54425 |
Banana streak UL virus taxid:1016856
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| P24 | ma-jd-viral-03107 |
| Virion associated protein | ma-jd-viral-54426 |
Banana streak UM virus taxid:1016857
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| P24 | ma-jd-viral-03111 |
| Virion associated protein | ma-jd-viral-54424 |
Banana streak VN virus taxid:1411991
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-03105 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-05988 |
Banana streak virus Acuminata Yunnan taxid:334778
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ORFI | ma-jd-viral-03109 |
| ORFII | ma-jd-viral-05989 |
Cacao mild mosaic virus taxid:1940252
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| P1 protein | ma-jd-viral-03093 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-06004 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-66245 |
Cycad leaf necrosis virus taxid:549205
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ORF1 | ma-jd-viral-03115 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-06001 |
Dahlia mosaic virus taxid:213888
Dioscorea bacilliform virus taxid:52996
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ORF1 protein | ma-jd-viral-03102 |
Dracaena mottle virus taxid:380669
Fig badnavirus 1 taxid:1034096
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| DNA-binding protein | ma-jd-viral-06006 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-03073 |
Gooseberry vein banding associated virus taxid:157270
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| P2 | ma-jd-viral-06021 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-47160 |
Grapevine Roditis leaf discoloration-associated virus taxid:1471299
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| P2 | ma-jd-viral-06002 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-03077 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-12028 |
Grapevine vein clearing virus taxid:1050407
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-06024 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-47162 |
Hibiscus bacilliform virus GD1 taxid:1459800
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Polyprotein | ma-jd-viral-12027 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-03096 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-06008 |
Horseradish latent virus taxid:264076
Lamium leaf distortion virus taxid:515320
Mulberry badnavirus 1 taxid:1227557
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-12025 |
Pagoda yellow mosaic associated virus taxid:1505530
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-01514 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-06022 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-34691 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-46382 |
Peanut chlorotic streak virus taxid:35593
Pelargonium vein banding virus taxid:671126
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| P1 | ma-jd-viral-03076 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-06005 |
Piper yellow mottle virus taxid:262957
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ORF1 | ma-jd-viral-03084 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-06003 |
| ORF4 | ma-jd-viral-29450 |
Rose yellow vein virus taxid:1213588
Rubus yellow net virus taxid:198310
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Coat protein | ma-jd-viral-41846 |
| Secreted protein | ma-jd-viral-34114 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-06025 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-47163 |
Rudbeckia flower distortion virus taxid:587370
Soybean Putnam virus taxid:1221449
Strawberry vein banding virus taxid:47903
Sugarcane bacilliform Guadeloupe D virus taxid:1960253
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ORF1 protein | ma-jd-viral-03099 |
| ORF2 protein | ma-jd-viral-05995 |
Sweet potato badnavirus B taxid:647294
Sweet potato collusive virus taxid:930168
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Coat protein/movement protein | ma-jd-viral-46551 |
| Putative inclusion body protein | ma-jd-viral-11140 |
| RNA-directed DNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.49) | ma-jd-viral-66576 |
Sweet potato vein clearing virus taxid:995049
Taro bacilliform CH virus taxid:1634914
Water chestnut soymovirus 1 taxid:1848040
Yacon necrotic mottle virus taxid:1561150
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ORF1 | ma-jd-viral-03071 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-06013 |
| ORF4 | ma-jd-viral-66244 |
