Ruflodivirus (taxid:2843011)
VIRION
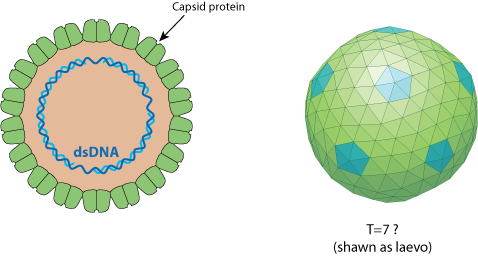
Non enveloped, large (50 nm diameter) icosahedral particles composed of 420 subunits with a T=7 symmetry  .
It has not been described whether handedness of capsid is laevo or dextro, here the pictures displays a laevo form.
.
It has not been described whether handedness of capsid is laevo or dextro, here the pictures displays a laevo form.
GENOME
Monopartite, open circular, double stranded DNA of about 8000 base pairs with discontinuities in both strands: one in the transcribed strand and one to three in the non-transcribed strand. Codes for 7 proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
The genomic RNA and its spliced derivatives serves as polycistronic mRNA for viral proteins. Polycistronic translation may depends on ORF4(Tav) which is would be a translation reinitiation factor.
ENZYMES
- Reverse transcriptase
- RNAse H [RT]
- Polyprotein protease (Peptidase A3) [PRO]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC / NUCLEAR
- Attachment of viral proteins to host receptors mediates entry into the host cell.
- The viral dsDNA is released into the nucleus.
- Transcribed by host RNA polymerase II.
- mRNA translation produces viral proteins.
- Genomic RNA is retrotranscribed into new dsDNA genomes in the cytoplasm.
- Genomes are encapsidated by the capsid protein and form new virions.
- The virion infects either a new cell by plasmodesmata movement, or by insect vector uptake.
