Betanucleorhabdovirus (taxid:2733248)
VIRION
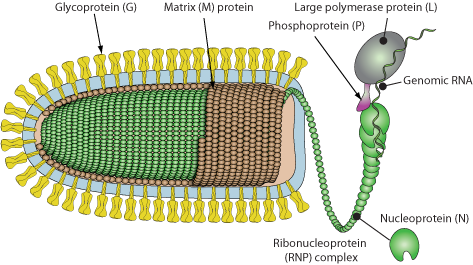
Enveloped, bullet shaped. 180 nm long and 75 nm wide. Certain plant rhabdoviruses are bacilliform in shape and almost twice the length.
GENOME
Negative-stranded RNA linear genome, about 11-15 kb in size. Encodes for 5 to six proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
The viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase binds the encapsidated genome at the leader region, then sequentially transcribes each genes by recognizing start and stop signals flanking viral genes. mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by the L protein during synthesis.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase L
- Mononega-type capping
- RNA TPase, GTase, N7 Mtase, 2'O Mtase L
REPLICATION
IN PLANT:NUCLEAR
- Virus penetrates into the cell by effraction or plasmodesmata transport.
- Viral nucleocapsid is transported into the host nucleus
- Sequential transcription , viral mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by polymerase stuttering in the cytoplasm.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- The ribonucleocapsid can penetrate in neighboring plant cells through plasmodesmata transport
- Alternatively the ribonucleocapsid can binds to the matrix protein and budding of particles occurs at the cell membrane, releasing new virions.
IN INSECT:NUCLEAR
- Attachment of the viral G glycoproteins to host receptors.
- Fusion of virus membrane with the vesicle membrane; ribonucleocapsid is released into the cytoplasm.
- Viral nucleocapsid is transported into the host nucleus
- Sequential transcription , viral mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by polymerase stuttering in the cytoplasm.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- The ribonucleocapsid binds to the matrix protein and budding of particles occurs at the cell membrane, releasing new virions.
Host-virus interaction
Movement through plasmodesmata
Viral movement protein 3of RYSV presumably interacts with host plasmodesmata to allow tubule guided movement of viral genomic material from cell to cell without budding. 
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)6 entries grouped by strain
6 entries
