Viral budding via the host ESCRT complexes (kw:KW-1187)

 .
.
ESCRT complexes are normally used by the cell for biological functions involving membrane remodeling, such as intraluminal vesicle formation, autophagy or terminal stages of cytokinesis  . The ESCRT family consists of ESCRT-0, ESCRT-I, ESCRT-II which are primarily involved in cargo sorting and membrane deformation, and ESCRT-III which cleaves the bud neck from its cytosolic face
. The ESCRT family consists of ESCRT-0, ESCRT-I, ESCRT-II which are primarily involved in cargo sorting and membrane deformation, and ESCRT-III which cleaves the bud neck from its cytosolic face  . In the last step, vps4 disassembles the complex. The budding reaction catalyzed by the ESCRT machinery has reversed topology when compared with most other budding processes in the cell, such as endocytosis and formation of transport vesicles.
. In the last step, vps4 disassembles the complex. The budding reaction catalyzed by the ESCRT machinery has reversed topology when compared with most other budding processes in the cell, such as endocytosis and formation of transport vesicles.
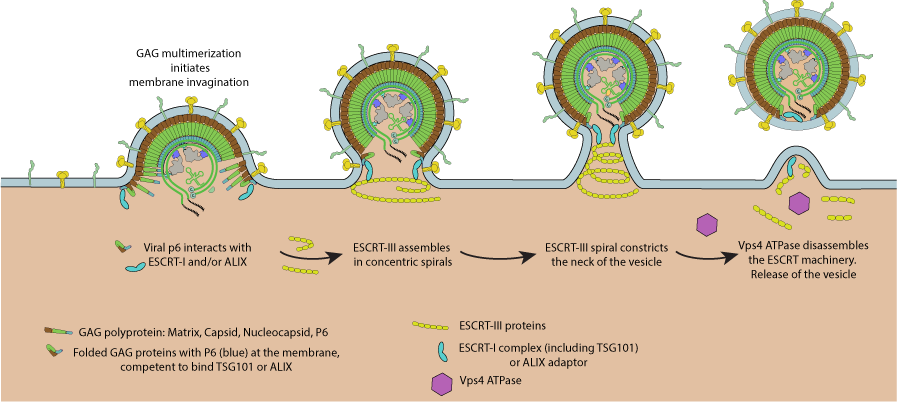
Specific motifs in viral proteins called late assembly domains (L-domains) are responsible for recruiting the host ESCRT machinery directly or via ESCRT-associated proteins like ALIX.
- P(T/S)AP motif recruits the ESCRT machinery via TSG101.
- PPxY motif enlists members of the NEDD4 family of ubiquitin ligases through interactions with WW domains, although the precise link between the NEDD4-like proteins and the ESCRT machinery is still unknown.
- ΘPxV where Θ is a hydrophobic amino acid.
- YP(x)n L binds the adaptor protein ALIX, which in turn binds and recruits the ESCRT machinery.
Some enveloped viruses however seem to use other mechanisms to bud, as it has been shown for Influenza virus  .
.
Viruses budding through the ESCRT machinery:
| Family | Virus | Viral protein | L-domain motif | Host ESCRT | Budding location | ref |
| Retroviridae | HIV-1 | P6-gag | PTAP | TSG101 | Cell membrane |


|
| LYPx<sub>nL | ALIX (low affinity) | Cell membrane |


|
|||
| SIV | P6-gag | PTAP | TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
|
| LYPx<sub>nL | ALIX | Cell membrane |

|
|||
| HTLV-1 | P19-gag | PPxY | NEDD4 | Cell membrane |


|
|
| PTAP | TSG101 (low affinity) | Cell membrane |

 |
|||
| Human spumaretrovirus | Gag protein | PTAP | TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
|
| Moloney murine leukemia virus | P12-gag | PPxY | ITCH | Cell membrane |

|
|
| PTAP | TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
|||
| LYPx<sub>nL | ALIX | Cell membrane |

|
|||
| Bovine leukemia virus | Gag protein | PPxY<sub>nL | NEDD4 | Cell membrane |

|
|
| Rous sarcoma virus | Gag protein | PPxY | NEDD4 | Cell membrane |


|
|
| Mason-Pfizer monkey virus | Gag protein | PSAP | TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
|
| PPxY | NEDD4 | Cell membrane |

|
|||
| EIAV | P9-gag | LYPx<sub>nL | ALIX | Cell membrane |

|
|
| Hepadnaviridae | HBV | ? Capsid protein | ? | ALIX | Endoplasmic reticulum |

|
| Filoviridae | Ebolavirus | Matrix protein | PTAP | TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
| PPxY | NEDD4 | Cell membrane |

|
|||
| Marburgvirus | Matrix protein | PPxY | NEDD4 | Cell membrane |

|
|
| Nucleoprotein | PSAP | TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
||
| Rhabdoviridae | Vesicular stomatitis virus | M protein | PPxY | NEDD4 | Cell membrane |

|
| ?PSAP | ? TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
|||
| Rabies virus | M protein | PPxY | NEDD4 | Cell membrane |

|
|
| Paramyxoviridae | Sendai virus | M protein | YLDL | ALIX | Cell membrane |

|
| Newcastle disease virus | M protein | FPIV | ? | Cell membrane |

|
|
| Nipah virus | M protein | YMYL | ALIX | Cell membrane |

|
|
| C protein | ? | TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
||
| Simian virus 5 | M protein | FPIV | ? | Cell membrane |

|
|
| Mumps virus | M protein | FPVI | ? | Cell membrane |

|
|
| Arenaviridae | Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus | Z protein | PPPY | NEDD4 | Cell membrane | |
| ? | ? | TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
||
| Lassa virus | Z protein | PTAP | TSG101 | Cell membrane |

|
|
| PPxY | NEDD4 | Cell membrane |

|
|||
| Bunyaviridae | Gn glycoproteins | ?YxxL | ? ALIX | Golgi |

|
|
| Flaviviridae | Hepatitis C virus | ? Core protein | ? | ? | Endoplasmic reticulum |


|
| Herpesviridae | Herpes simplex virus 1 | ? | ? | Vps4 | Trans-Golgi |

|
| Epstein-Barr virus | ? | ? | ? | Trans-Golgi |

|
|
| HCMV | ? | ? | Vps4 | Trans-Golgi |

|
|
| Poxviridae | Vaccinia virus | F13 protein | LYPx(n)L | ? | Cell membrane |

|
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by strain
