Viral penetration into host cytoplasm (kw:KW-1162)
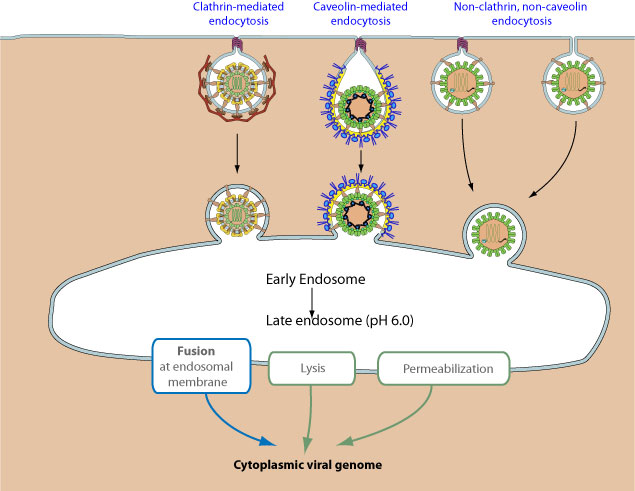
Translocation of the virion or its genetic material from the extracellular space into the host cell cytoplasm. Entry is achieved through pore formation, membrane fusion and/or endocytosis mechanisms.
Penetration reactions occur mainly in five locations: the cell
membrane, early and late endosomes, caveosomes, and the ER. Many viruses are able to utilize multiple uptake pathways, simultaneously, or depending on the host cell type targeted.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by strain
