Betaarterivirus (taxid:2499674)
VIRION
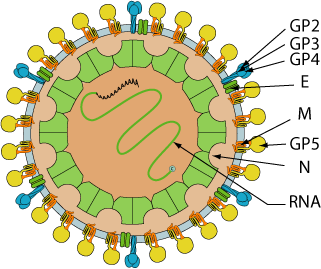
Enveloped, spherical, about 45-60 nm in diameter. The virion is comprised of an isometric core of 20-30 nm surrounded by a lipid-containing envelope. The RNA genome associates with the N protein to form the nucleocapsid.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, ssRNA(+) genome of 14-16kb in size, capped, and polyadenylated. The leader RNA (65-89 bp) at the 5' end of the genome is also present at the end of each subgenomic RNAs. Enzymes: EndoU ribonuclease
GENE EXPRESSION
The virion RNA is infectious and serves as both genome and viral messenger RNA. ORF1b is translated by a ribosomal frameshifting. Polyproteins pp1a and pp1ab are processed into the viral polymerase (RdRp) and other non-structural proteins involved in RNA synthesis. Structural proteins are expressed as subgenomic RNAs. The mRNA2 is bicistronic. PRRSV also expresses a truncated polyprotein 1aTF due to a ribosomal frameshifting in the nsp2 gene.
Protein GP2 and 5a are produced by leaky scanning from the E and gp5 subgenomic mRNA respectively.
ENZYMES
- RNA-directed RNA polymerase [Q04561]
- Nido-type capping (GDP polyribonucleotidyltransferase, N7methyltransferase, 2'O methylase) [Q04561]
- EndoU ribonuclease [Q04561]
- Polyprotein major protease (Peptidase S32) [Q04561]
- Proteases (Peptidase C31, Peptidase C32, Peptidase C33) [Q04561]
- Helicase [Q04561]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachement to host receptors mediates clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion of virus membrane with the endosomal membrane. ssRNA(+) genome is released into the cytoplasm.
- Synthesis and proteolysis of replicase polyproteins.
- Replication occurs in viral factories. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+).
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- Synthesis of structural proteins encoded by subgenomic mRNAs.
- assembly and ESCRT-independent budding at the membranes of endoplasmic reticulum (ER), intermediate compartments, and/or Golgi complex.
- Release of new virions by exocytosis.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
PRRSV induces apoptosis via host caspases activation (caspase-8 and mitochondria-dependent caspase-9)

Autophagy modulation
PRRSV induces autophagy to promote virus replication


 .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
PRRSV clearly inhibits the type-I IFN response and down-regulates TLR3, TLR7, and TLR8 expression.
At least three non-structural proteins (Nsp1, Nsp2, and Nsp11) play roles in the IFN suppression and NF-κB pathways

 :
:
Nsp1α subunit inhibits the IκB phosphorylation in the cytoplasm and therefore the activation of NF-κB.
Nsp1β inhibits phosphorylation of STAT1 and nuclear translocation of ISGF3 complex (composed of STAT1, STAT2 and IRF9).
Nsp1β prevents IRF3 activation, thereby interfering with the RIG-I signaling pathway

 .
.
Nsp2 inhibits IFN production by blocking the ubiquitinylation of phosphorylated IκB and phosphorylation of IRF3 through the OTU domain. Nsp2 has the potential to deconjugate ISGylation.
Nsp11 suppresses IFN-β production through degradation of IPS-1 mRNA. For the second wave of IFN signaling, PRRSV Nsp1β blocks the phosphorylation of STATs and inhibits the nuclear translocation of ISGF3 complex (composed of STAT1, STAT2 and IRF9).
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)24 entries grouped by protein
1 entry
Truncated polyprotein 1aTF
2 entries
Envelope small membrane protein (Protein E) (Glycoprotein 2b) (Protein GP2b) (Gs)
2 entries
Glycoprotein 2a (Protein GP2a) (GP2)
2 entries
Glycoprotein 3 (Protein GP3)
2 entries
Glycoprotein 4 (Protein GP4)
2 entries
Glycoprotein 5 (Protein GP5) (G(L))
2 entries
Membrane protein (Protein M)
2 entries
Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) (Protein N)
2 entries
Structural protein ORF5a
6 entries
Replicase polyprotein 1ab (ORF1ab polyprotein)
1 entry
