DNA-dependent DNA polymerase

Naming: By convention viral polymerases are called RNA/DNA-dependent whereas cellular polymerases are called RNA/DNA-directed.
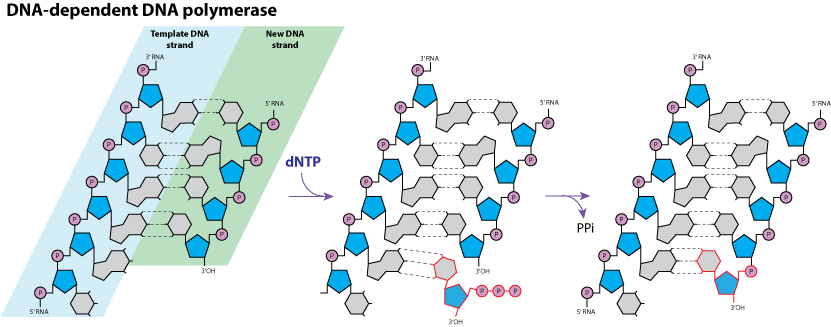
Enzymatic reaction:
- DNA nucleotidyltransferase (DNA-dependent) EC 2.7.7.7 RHEA:22508
 . Subsequently, the 3'-oxygen acts as a nucleophile to attack the phosphate bond and eventually releases a pyrophosphate.
. Subsequently, the 3'-oxygen acts as a nucleophile to attack the phosphate bond and eventually releases a pyrophosphate.
Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements
O Poch 1, I Sauvaget, M Delarue, N Tordo
EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867-74
A Structural Overview of RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases from the Flaviviridae Family
Jiqin Wu, Weichi Liu, and Peng Gong
Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jun; 16(6): 12943?12957
The logic of DNA replication in double-stranded DNA viruses: insights from global analysis of viral genomes
Darius Kazlauskas, Mart Krupovic, Ceslovas Venclovas
Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jun 2;44(10):4551-64.
| Family | Primer | Domain | Viruses | Cells | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA_A | RNA | IPR002298 | dsDNA bacteria viruses:(Caudoviricetes) | Bacteria | |
| DNA_B | RNA | IPR006172 | dsDNA bacteria and archaea viruses:(Caudoviricetes, Preplasmiviricota) dsDNA eukaryotic viruses:(Nucleocytoviricota, Preplasmiviricota, Herpeviricetes, Naldaviricetes) | Eukaryotes and archaea | |
| pDNA_B | Protein-priming | dsDNA viruses: Tectiliviricetes | None | No helicases, but unique SSB | |
| DNA_C | RNA | dsDNA viruses: (Caudoviricetes) | Bacteria |
Data adapted from: The logic of DNA replication in double-stranded DNA viruses: insights from global analysis of viral genomes
Darius Kazlauskas, Mart Krupovic, Ceslovas Venclovas;
Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jun 2;44(10):4551-64.
