VIRION
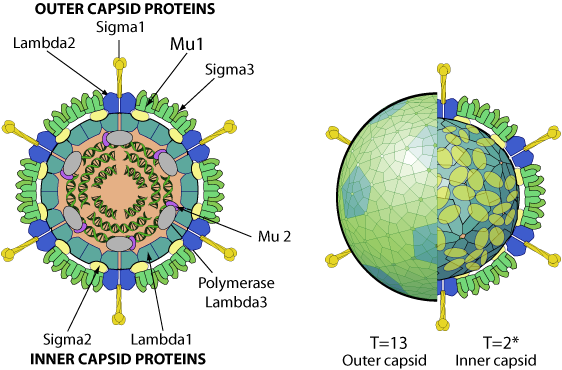
Non enveloped, icosahedral virion with a double capsid structure, about 80 nm in diameter. Pentameric turrets sit on the outside of the innermost capsid. The outer capsid has a T=13 icosahedral symmetry, the inner capsid a T=2* icosahedral symmetry.
Virion maturation schemes
GENOME
Segmented dsRNA linear genome. Contains 10 segments: L1, L2, L3, M1, M2, M3, S1, S2, S3, S4, coding for 12-13 proteins. Segments size range from 1,189 to 3,916nt (MRV-3De). Genome total size is 23.5 Kb (MRV-3De). MuNSC and S.1s are produced by leaky scanning of mRNA M3 and S1 respectively.
GENE EXPRESSION
The dsRNA genome is never completely uncoated, to prevent activation of antiviral state by the cell in response to dsRNA. The viral polymerase lambda3 synthesizes a capped and non-polyadenylated monocistronic mRNA from each dsRNA segment. These capped mRNAs are translocated to the cell cytoplasm where they are translated.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [Lambda3]
- Cell-type capping:
- Helicase [Lambda1]
- Self-cleavage, Virion maturation (Peptidase N7) [Mu1]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachment to host receptors mediates clathrin-mediated endocytosis of virus into host cell.
- Particles are partially uncoated in endolysosomes, but not entirely, and penetrate in the cytoplasm.
- Early transcription of the dsRNA genome by viral polymerase occurs inside this sub-viral particle (naked core), so that dsRNA is never exposed to the cytoplasm.
- Full-length plus-strand transcripts from each of the dsRNA segments are synthesized. These plus-strand transcripts are used as templates for translation.
- Viral proteins and genomic RNAs aggregates in cytoplasmic viral factories.
- (+)RNAs are encapsidated in a sub-viral particle, in which they are transcribed to give RNA (-) molecules with which they become base-paired to produce dsRNA genomes.
- The capsid is assembled on the sub-viral particle.
- Mature virions are released presumably following cell death and associated breakdown of host plasma membrane.


