Chymotrypsin fold
Chymotrypsin-fold proteases feature a conserved core of two beta-barrels that ensure structural stability and are essential for catalytic function.
Origin
The chymotrypsin fold occurs across all cellular life forms and many viruses, indicating an evolutionary origin that likely predates the Last Universal Cellular Ancestor (LUCA) .
Topology
The chymotrypsin fold core is composed of two beta-barrels, with the catalytic triad (His?(Asp/Glu)?(Ser/Cys)) located at their interface . The extensions and loops connecting the ?-strands vary among members and confer specific functions, such as ligand recognition and binding.
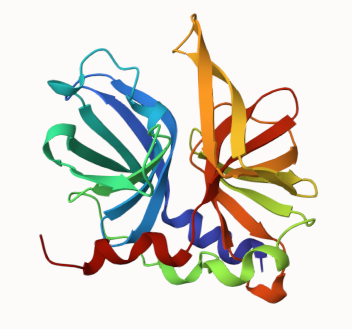
Hepatitis A virus 3C protease 1HAV
