Mupapillomavirus (taxid:334202)
VIRION
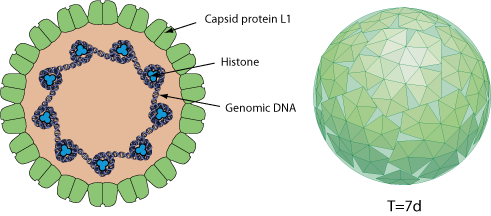
Non-enveloped. Small, icosahedral, about 52-55 nm in size. A single molecule of circular dsDNA is contained within the T=7 icosahedral capsid, which is composed of 72 pentamers.
GENOME
Circular dsDNA, about 8 kb in size, associated with cellular histones. On rare non-specific recombination, the viral genome can be integrated in host chromosome. This inactivates the integrated virus but can gives the host cell a replicative advantage sometimes leading to malignant tumours.
GENE EXPRESSION
Only one strand of the genome is transcribed and yield two classes of proteins expressed by alternative splicing :
a) Early Proteins: non-structural regulatory proteins (E1-E7).
b) Late Proteins: the structural proteins L1 and L2.
REPLICATION
NUCLEAR
Replication is divided in two distinct steps  that are linked to the differentiation state of the host epithelial cell:
that are linked to the differentiation state of the host epithelial cell:
a) The plasmid replication takes place in the basal squamous epithelial cells. It corresponds to viral DNA replication in synchrony with the host cell chromosome in order to ensures an average of one viral genome per basal cell.
- Attachment of the viral proteins to host receptors mediates endocytosis into vesicles in the basal squamous epithelial cell.
- Transport to the nucleus and uncoating of the viral DNA.
- Early-region transcription and translation of the early proteins.
- Steady-state viral DNA nuclear replication. Requires the origin of DNA replication in cis and the viral E1 and E2 proteins in trans.
b) The vegetative replication, which occurs in differentiated keratinocytes. In these cells, which no longer undergo cellular DNA synthesis, there is a burst of viral DNA synthesis with active production of virions.
- Vegetative viral DNA synthesis.
- Transcription of the late region.
- Capsid proteins L1 and L2 synthesis.
- Nuclear capsid assembly and release of viruses.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)15 entries grouped by protein
2 entries
Replication protein E1 (EC 5.6.2.4) (ATP-dependent helicase E1) (DNA 3'-5' helicase E1)
2 entries
Regulatory protein E2
2 entries
Protein E4
2 entries
Protein E6
2 entries
Protein E7
1 entry
Protein E8^E2C
2 entries
Major capsid protein L1
2 entries
Minor capsid protein L2
Human papillomavirus type 1 taxid:10583
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| E8 protein | ma-jd-viral-49300 |
| Major capsid protein L1 | ma-jd-viral-67270 |
| Minor capsid protein L2 | ma-jd-viral-44894 |
| Protein E6 | ma-jd-viral-00962 |
| Protein E7 | ma-jd-viral-13700 |
