Rhabdoviridae (taxid:11270)
VIRION
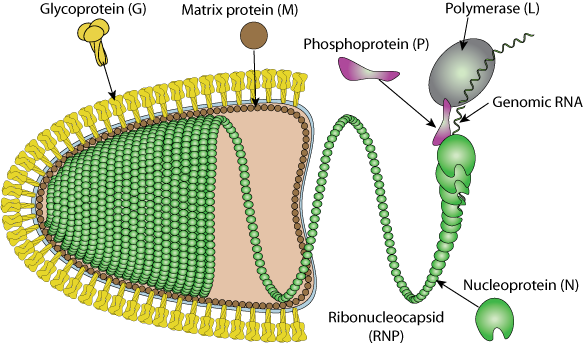
Enveloped, bullet shaped. 180 nm long and 75 nm wide. Certain plant rhabdoviruses are bacilliform in shape and almost twice the length.
GENOME
Negative-stranded RNA linear genome, about 11-15 kb in size. Varicosavirus genomes consists in two segments. Encodes for 5 to six proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
The viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase binds the encapsidated genome at the leader region, then sequentially transcribes each genes by recognizing start and stop signals flanking viral genes. mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by the L protein during synthesis.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase L"
- Mononega-type capping
- RNA TPase, GTase, N7 Mtase, 2'O Mtase L"
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachement of the viral G glycoproteins to host receptors mediates Clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion of virus membrane with the vesicle membrane; ribonucleocapsid is released into the cytoplasm.
- Sequential transcription , viral mRNAs are capped and polyadenylated by polymerase stuttering in the cytoplasm.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- The ribonucleocapsid binds to the matrix protein and buds via the host ESCRT complexes occurs at the plasma membrane, releasing new virions.
Host-virus interaction
Host gene expression shutoff
Vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein blocks nuclear pores, resulting in host mRNA nuclear export inhibiton
This shutoff of host gene expression prevents effective antiviral response by the infected cell.

Inhibition of host Interferon induction
Rabies nucleoprotein plays a role in inhibition of RIG-I antiviral signaling  Rabies phosphoprotein may inhibit IRF-3 phosphorylation
Rabies phosphoprotein may inhibit IRF-3 phosphorylation 
Inhibition of host type I interferon signaling
Rabies phosphoprotein may inhibit STAT-I antiviral pathway signaling by preventing nuclear localization of STAT dimers upon activation. 
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by protein
Adelaide River virus taxid:31612
Alfalfa dwarf virus taxid:998864
Almpiwar virus taxid:318843
Australian bat lyssavirus (isolate Bat/AUS/1996) taxid:446561
Beihai barnacle virus 7 taxid:1922365
Berrimah virus taxid:318834
Bole Tick Virus 2 taxid:1608041
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65399 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11599 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15152 |
| Putative phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-64349 |
Chandipura virus taxid:11272
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07124 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11579 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15201 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-41126 |
Chandipura virus (strain I653514) taxid:11273
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11579 |
Coastal Plains virus taxid:764599
Culex tritaeniorhynchus rhabdovirus taxid:936308
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07054 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-03356 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15095 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-40129 |
Datura yellow vein nucleorhabdovirus taxid:195059
Diachasmimorpha longicaudata rhabdovirus taxid:1585246
Dolphin rhabdovirus taxid:1511639
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07071 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11665 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15126 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-32193 |
Drosophila melanogaster sigma virus (isolate Drosophila/USA/AP30/2005) taxid:666363
Drosophila obscura sigmavirus 10A taxid:666962
Duvenhage virus taxid:38767
Eel virus European X taxid:685443
Eggplant mottled dwarf virus taxid:488317
European bat lyssavirus 1 taxid:57482
European bat lyssavirus 1 (strain Bat/Germany/RV9/1968) taxid:453115
European bat lyssavirus 2 taxid:57483
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07135 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein P) (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-47494 |
European bat lyssavirus 2 (strain Human/Scotland/RV1333/2002) taxid:453116
Farmington virus taxid:1027468
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| G | ma-jd-viral-56491 |
| M | ma-jd-viral-53670 |
| N | ma-jd-viral-40454 |
| P | ma-jd-viral-49469 |
Fikirini virus taxid:1408144
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07072 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11705 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15205 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-32357 |
Fox fecal rhabdovirus taxid:1504569
Gannoruwa bat lyssavirus taxid:1846259
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07145 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-62212 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15326 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein P) (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-47497 |
Gata virus taxid:1911435
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07090 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11660 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15089 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-45598 |
Huangpi Tick Virus 3 taxid:1608049
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65172 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15134 |
| Putative matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-34583 |
| Putative phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-45053 |
Hubei dimarhabdovirus 1 taxid:2849739
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15147 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-58265 |
| Putative glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07069 |
| Putative matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11715 |
Hubei diptera virus 10 taxid:1922871
Hubei diptera virus 9 taxid:1922889
Hubei lepidoptera virus 2 taxid:1922904
Hubei rhabdo-like virus 9 taxid:1923193
Ikoma lyssavirus taxid:1167696
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07138 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-62214 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15323 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein P) (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-47498 |
Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus taxid:11290
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65387 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11670 |
Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (strain WRAC) taxid:429314
Inhangapi virus taxid:1620892
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| G | ma-jd-viral-07027 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11644 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15188 |
| P | ma-jd-viral-62877 |
| PAG1 | ma-jd-viral-49703 |
Isfahan virus taxid:290008
Kimberley virus taxid:318835
Koolpinyah virus taxid:1550518
Kotonkan virus taxid:318836
Kumasi rhabdovirus taxid:1537975
Lagos bat virus taxid:38766
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07144 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-62211 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15317 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein P) (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-47501 |
Lettuce necrotic yellows virus (isolate 318) taxid:928304
Lettuce yellow mottle virus taxid:471285
Lleida bat lyssavirus taxid:1213198
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07141 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-62218 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15319 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein P) (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-47492 |
Long Island tick rhabdovirus taxid:1459044
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65388 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15094 |
| Putative matrix | ma-jd-viral-11605 |
| Putative phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-55616 |
Lyssavirus bokeloh taxid:1072176
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07142 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-62217 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15322 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein P) (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-47496 |
Lyssavirus shimoni taxid:746543
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07148 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-62221 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15321 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein P) (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-47493 |
Malakal virus taxid:1229186
Mokola virus taxid:12538
Moussa virus taxid:698672
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65405 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15127 |
| ORF2 protein | ma-jd-viral-36987 |
| ORF3 protein | ma-jd-viral-11606 |
Oak-Vale virus taxid:318852
Obodhiang virus taxid:380160
Orgi virus taxid:1911434
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07127 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11656 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15105 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-40038 |
Persimmon virus A taxid:1211480
Puerto Almendras virus taxid:1479613
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| G protein | ma-jd-viral-56581 |
| M protein | ma-jd-viral-11544 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15141 |
| P protein | ma-jd-viral-44088 |
| SH protein | ma-jd-viral-59396 |
Rabies virus taxid:11292
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07137 |
Rabies virus (strain Pasteur vaccins / PV) taxid:103929
Santa barbara virus taxid:1552661
Sanxia Water Strider Virus 5 taxid:1608064
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-62608 |
| Nucleoprotein (NP) (Protein N) (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15234 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-60137 |
| ORF3 | ma-jd-viral-11716 |
Scophthalmus maximus rhabdovirus taxid:936149
Shayang Fly Virus 2 taxid:1608066
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07062 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11661 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15081 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-49493 |
| X protein | ma-jd-viral-38965 |
Shayang Fly Virus 3 taxid:1608067
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-67030 |
| Nucleoprotein (NP) (Protein N) (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15312 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-41261 |
| ORF3 | ma-jd-viral-11724 |
Shayang ascaridia galli virus 2 taxid:1923460
Siniperca chuatsi rhabdovirus taxid:373862
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| G protein | ma-jd-viral-07096 |
| M protein | ma-jd-viral-11668 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15117 |
| P protein | ma-jd-viral-32192 |
Snakehead rhabdovirus taxid:103603
Sonchus yellow net virus taxid:11307
Spodoptera frugiperda rhabdovirus taxid:1481139
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| G | ma-jd-viral-33379 |
| M | ma-jd-viral-33113 |
| Nucleoprotein (NP) (Protein N) (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15073 |
| P | ma-jd-viral-46064 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ma-jd-viral-35015 |
Spring viremia of carp virus taxid:696863
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11551 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11551 |
Sprivivirus esox taxid:219584
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07113 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11552 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15168 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-33212 |
Sunguru virus taxid:1491491
Tacheng Tick Virus 3 taxid:1608085
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| ORF1 | ma-jd-viral-11612 |
Tacheng Tick Virus 7 taxid:1608089
Taishun Tick Virus taxid:1608090
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15206 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-43362 |
Tench rhabdovirus taxid:1288358
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07122 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11553 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15142 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-33215 |
Tibrogargan virus (strain CS132) taxid:1559361
Tongilchon virus 1 taxid:1758878
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11652 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15194 |
| Putative glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65398 |
| Putative phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-33123 |
Vesicular stomatitis Alagoas virus taxid:198833
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07111 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11573 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15092 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-41128 |
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus taxid:11277
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15153 |
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain 98COE North America) taxid:434488
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Nucleoprotein (NP) (Nucleocapsid protein) (Protein N) | ma-jd-viral-15153 |
Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (strain San Juan) taxid:11285
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Matrix protein (M protein) | ma-jd-viral-11572 |
| Nucleoprotein (NP) (Nucleocapsid protein) (Protein N) | ma-jd-viral-15153 |
| Phosphoprotein (P protein) (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-41125 |
Vesicular stomatitis New Jersey virus taxid:11280
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07057 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11574 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15178 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein M1) | ma-jd-viral-41130 |
Walkabout Creek virus taxid:1569258
Wenling crustacean virus 10 taxid:1923479
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-30325 |
| Nucleoprotein (NP) (Protein N) (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15074 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-41079 |
| Putative glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-42330 |
Wenling crustacean virus 11 taxid:1923480
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-50426 |
| Nucleoprotein | ma-jd-viral-15077 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-40764 |
| Putative glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-42329 |
Wuhan Fly Virus 2 taxid:1608102
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07085 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11664 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15156 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-49492 |
| X protein | ma-jd-viral-38968 |
Wuhan House Fly Virus 1 taxid:1608104
Wuhan House Fly Virus 2 taxid:1608105
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-67029 |
| Nucleoprotein (NP) (Protein N) (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15311 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-51497 |
| ORF3 | ma-jd-viral-11725 |
Wuhan Insect virus 4 taxid:1608109
Wuhan Insect virus 5 taxid:1608110
Wuhan Insect virus 6 taxid:1608111
Wuhan Insect virus 7 taxid:1608112
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07045 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11638 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15106 |
| Putative phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-34592 |
Wuhan Louse Fly Virus 10 taxid:1608114
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07082 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11581 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15143 |
| Putative phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-49369 |
Wuhan Louse Fly Virus 5 taxid:1608119
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07101 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11696 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15186 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-32356 |
Wuhan Louse Fly Virus 9 taxid:1608123
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65404 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11580 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15091 |
| Putative phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65825 |
Wuhan Mosquito Virus 9 taxid:1608134
Wuhan Tick Virus 1 taxid:1608137
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15121 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-51899 |
| ORF3 | ma-jd-viral-11611 |
Xiburema virus taxid:1272959
Xingshan nematode virus 4 taxid:1923763
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-64062 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15160 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-59660 |
| Putative glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65393 |
Xinzhou nematode virus 4 taxid:1923772
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11739 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15123 |
| Phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-59892 |
| Putative glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-65403 |
Yata virus taxid:1272960
Yongjia Tick Virus 2 taxid:1608146
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-07108 |
| Matrix protein | ma-jd-viral-11701 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-15157 |
| Putative phosphoprotein | ma-jd-viral-29228 |
