Amdoparvovirus (taxid:310911)
VIRION
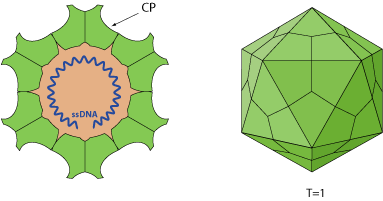
Non-enveloped, round, T=1 icosahedral symmetry, 18-26 nm in diameter. The capsid consists of 60 copies of CP protein.
GENOME
Linear, ssDNA genome (-) of about 4.8kb in size. Equal amount of positive and negative strands are encapsidated, although the percentage of particles encapsidating the positive strand can be lower depending on the host cell. ORFs for both the structural and non-structural proteins are located on the same DNA strand.
The genome is replicated through rolling-hairpin mechanism.
GENE EXPRESSION
Host proteins transcribe the genomes into mRNAs. Alternative mRNAs splicing allows expression of six different mRNAs.
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
NUCLEAR
- Attachement to host receptors initiates clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the virion into the host cell.
- The virion penetrates into the cytoplasm via permeabilization of host endosomal membrane.
- Microtubular transport of the virion toward the nucleus.
- The viral ssDNA genome penetrates into the nucleus.
- The ssDNA is converted into dsDNA by cellular proteins.
- dsDNA transcription gives rise to viral mRNAs when host cell enters S phase and translated to produce viral proteins.
- Replication occurs through rolling-hairpin mechanism, with NS1 endonuclease binding covalently to the 5' genomic end.
- Individual ssDNA genomes are excised from replication concatemers by a process called junction resolution.
- These newly synthesized ssDNA can either
a) be converted to dsDNA and serve as a template for transcription/replication
b) be encapsidated to form new virions that are released by cell lysis.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
AMDV induces apoptosis and caspases activation, which facilitate its replication by specifically cleaving viral NS-1 and capsid proteins. The cleavage products are crucial for the replication of the AMDV genome
 .
.
Cytopathic effect of BPV are probably mediated by necrosis rather than apoptosis.
Cell-cycle modulation
AMDV induces G2/M checkpoint arrest.

Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)4 entries grouped by protein
1 entry
Capsid protein VP1
1 entry
Initiator protein NS1 (NS1) (EC 3.1.21.-) (EC 3.6.4.12) (Non-structural protein 1) (Non-structural protein NS1)
1 entry
Non-structural protein NS2
1 entry
Non-structural protein NS3
Amdoparvovirus sp. taxid:1908805
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Initiator protein NS1 (EC 3.6.4.12) (Non-structural protein NS1) | ma-jd-viral-23459 |
| VP1 | ma-jd-viral-07356 |
Raccoon dog amdovirus taxid:1513315
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Initiator protein NS1 (EC 3.6.4.12) (Non-structural protein NS1) | ma-jd-viral-23457 |
| NS2 | ma-jd-viral-50510 |
| NS3 | ma-jd-viral-38762 |
| VP1 | ma-jd-viral-07378 |
| VP2 | ma-jd-viral-07360 |
