Inhibition of host IRF7 by virus (kw:KW-1093)
IRF7 is a key transcriptional factor involved in the signaling pathway leading to establishment of antiviral state in infected cells. Under normal conditions, IRF7 exists in a latent form in the cytoplasm. Viral infection triggers the phosphorylation of IRF7 C-terminal region. The activated IRF7 migrates to the nucleus leading to the transcriptional activation of the IFN-alpha and IFN-beta genes. IRF7 is predominantly expressed in the spleen, thymus and primary blood lymphocytes(PBL) as a lymphoid-specific factor.
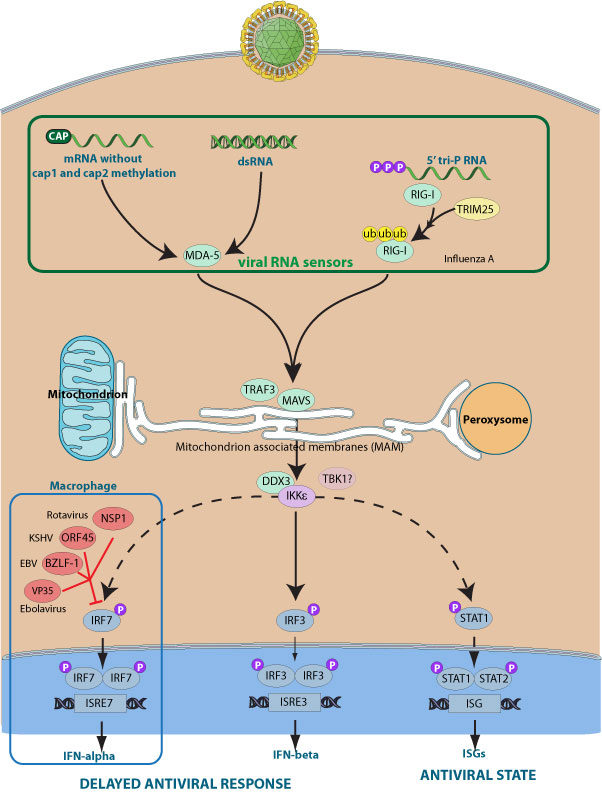
Several viral proteins interfere with IRF7 activity thus modulating the response to the virus induced in the infected cell. For example, VP35 from ebola virus exploits the cellular SUMOylation machinery for its advantage and increase IRF7 SUMOylation thereby disabling its activity.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)78 entries grouped by protein
3 entries
Protein MGF 360-11L
1 entry
Lytic switch protein BZLF1 (EB1) (Protein Z) (Trans-activator protein BZLF1) (Zta) (bZIP transcription factor ZEBRA)
1 entry
Protein E3 homolog (Protein E3L homolog)
1 entry
Protein ML (ML)
7 entries
Non-structural protein 1 (Non-structural protein 1C)
6 entries
Non-structural protein 2 (NS2) (Non-structural protein 1B)
41 entries
Non-structural protein 1 (NSP1) (NCVP2) (Non-structural RNA-binding protein 53) (NS53)
1 entry
Protein ORF45
4 entries
RNA-binding protein OPG065 (RNA-binding protein E3) (p25)
1 entry
Genome polyprotein
6 entries
Non-structural protein V
1 entry
Viral IRF4-like protein (vIRF-4)
5 entries
