Activation of host NF-kappa-B by virus (kw:KW-1074)
NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. In unstimulated cells, NF-kappa-B dimers are sequestered in the cytoplasm via physical association with NF-kappa-B inhibitory proteins, called I-kappa-Bs. Upon activation, NF-kappa-B separates from I-kappa-B and migrates to the nucleus to activate gene transcription.
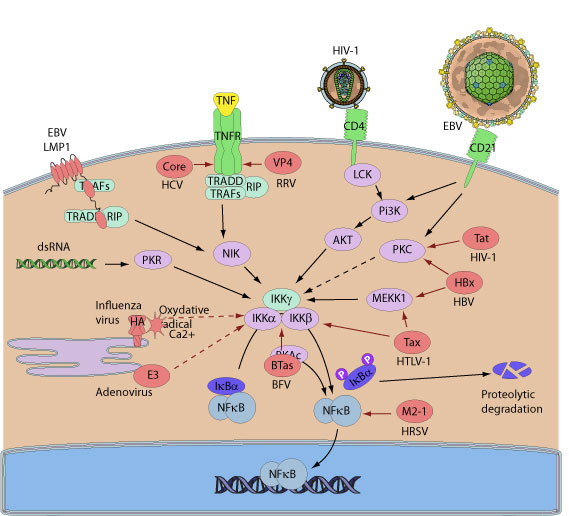
Multiple families of viruses have evolved sophisticated strategies to positively regulate nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling. Different viruses including HIV, herpesviruses, and HCV block apoptosis and prolong survival of the host cell in order to gain time for replication and increase viral progeny production. In addition, several oncogenic viruses are able to install a program of constitutive expression of NF-kB-dependent anti-apoptotic which results in cell transformation and uncontrolled proliferation.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)88 entries grouped by protein
11 entries
Inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP)
1 entry
Inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP)
3 entries
mRNA export factor (Immediate-early protein IE63) (Infected cell protein 27) (ICP27) (VMW63)
5 entries
Latent membrane protein 1 (LMP-1) (Protein p63)
4 entries
Protein M2-1 (Envelope-associated 22 kDa protein) (Transcription antitermination factor M2-1) (Vp24)
4 entries
Protein Tax-1 (Protein X-LOR) (Protein PX) (Trans-activating transcriptional regulatory protein of HTLV-1)
2 entries
Membrane glycoprotein UL144 (TNF alpha-like receptor UL144) (UL144 protein)
1 entry
Protein US2
1 entry
CARD domain-containing protein E10
1 entry
Viral FLICE protein (vFLIP)
55 entries
