Inhibition of host autophagy by virus (kw:KW-1083)
Autophagy is an evolutionary conserved mechanism for the sequestration and subsequent lysosomal degradation of discrete intracellular portions of eukaryotic cells, facilitating the removal of materials not degraded through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. In addition, autophagy plays important roles in innate and adaptive immune responses to pathogens.
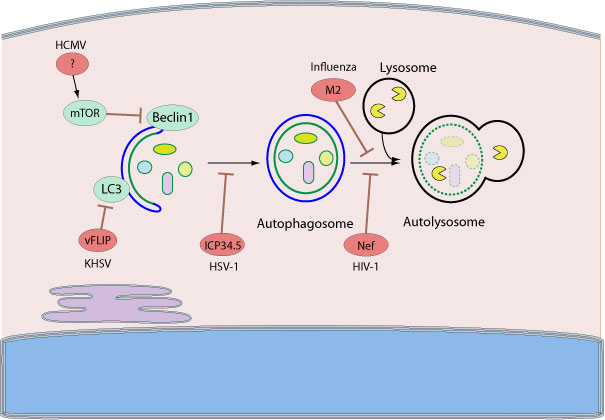
Several viruses have develop ways to subvert the pathway for their own benefit in order to avoid the immune response or to increase their viral replication. Beclin-1 is an essential autophagy protein and constitutes the major target for manipulation of autophagy by viruses. For example, HHV-1 ICP34.5 binds to Beclin-1 and inhibits autophagosome formation. HIV and Influenza A virus use the same mechanism through Nef and M2 respectively, that also interact with and inhibit host Beclin-1.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)175 entries grouped by protein
3 entries
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 homolog
1 entry
Viral CASP8 and FADD-like apoptosis regulator (v-CFLAR) (Viral FLICE-inhibitory protein) (v-FLIP)
3 entries
Apoptosis regulator BHRF1 (Early antigen protein R) (EA-R) (Nuclear antigen)
5 entries
Neurovirulence factor ICP34.5 (Infected cell protein 34.5) (protein gamma(1)34.5)
112 entries
Matrix protein 2 (Proton channel protein M2)
45 entries
Protein Nef (3'ORF) (Negative factor) (F-protein)
3 entries
Accessory factor US11 (Vmw21)
2 entries
Protein HHLF1
1 entry
