RNAse H
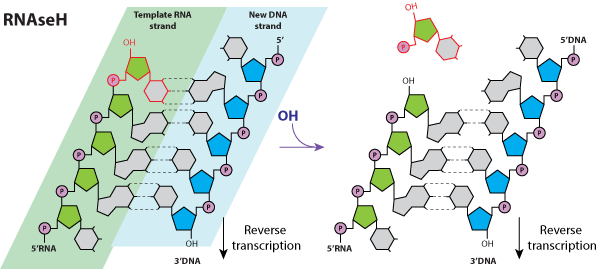
Enzymatic reaction:
- RNA-DNA duplex dependent endoribonuclease EC 3.1.26.4
Mechanism
Viral RNAse H are characterized by a conserved motif in which two conserved aspartic acid residues are bound to two magnesium ions. These ions interact with the phosphodiester bond. The reaction beginsby activation of a water molecule that acts as a nucleophile to attack the phosphate bond and eventually cleaves the phosphodiester bond, leaving a 3' hydroxyl and a 5' phosphate group.
