Alphatectivirus (taxid:2169669)
VIRION
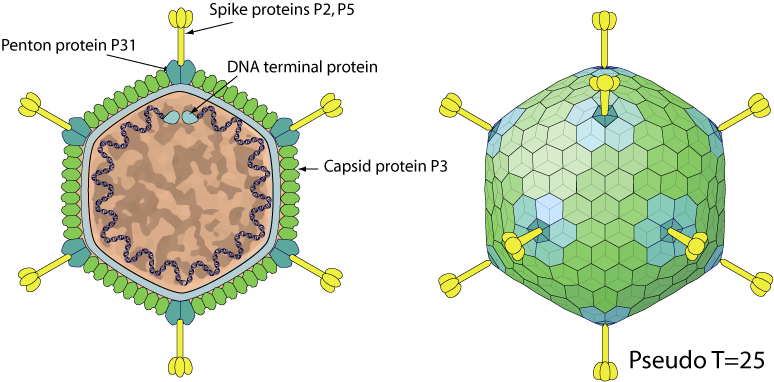
Non enveloped, icosahedral virion with a pseudo T=25 symmetry, consisting of 240 capsid proteins trimers. Virion size is about 66 nm with apical spikes of 20 nm. The capsid encloses a inner membrane vesicle within which the genomic DNA is coiled.
- Double jelly roll-fold major capsid protein [DJR-MCP]
- Single jelly roll-fold penton capsid protein [SJR-MCP]
GENOME
Linear, dsDNA genome of about 15 kb flanked by inverted repeats. Encodes for about 32 proteins. Replication is protein-primed.
GENE EXPRESSION
Genes are transcribed by operons.
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Adsorption: The phage attaches to target cell adhesion receptors through its spike protein P2. As a result, a protein complex composed of P2, P5, P31 and a part of the capsid (p3) is released, which produces a hole in the capsid.
- Internal phage membrane transforms into a tubular structure that protrudes through a hole in the capsid and penetrates the host outer membrane and peptidoglycan layer. This membrane tube then fuses with host plasma membrane, releasing the viral DNA into the cytoplasm.
- Transcription and translation of early genes.
- Replication of genomic DNA.
- Transcription and translation of late genes.
- Capsid proteins polymerize around a lipoprotein vesicle translocated in the cytoplasm by virion assembly factors.
- Genomic DNA is packaged in new virions.
- Mature virions are released from the cell by lysis.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)25 entries grouped by protein
1 entry
Major capsid protein P3 (Protein P3)
1 entry
DNA-directed DNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.7) (EC 3.1.11.-) (Protein P1)
1 entry
Endolysin (EC 3.2.1.17) (Beta-1,4-N-acetylmuramidase) (Lysozyme) (Lytic enzyme) (Muramidase) (Protein P15)
1 entry
Transglycosylase (EC 4.2.2.n1) (Protein P7)
1 entry
Holin (Protein P35)
1 entry
Adsorption protein P2 (Protein P2)
1 entry
Spike protein P5 (Protein P5)
1 entry
Packaging protein P20
1 entry
Packaging protein P22 (GpK) (Protein K)
1 entry
Packaging efficiency factor P6
1 entry
DNA packaging ATPase P9 (Protein P9)
1 entry
DNA terminal protein (Protein P8)
1 entry
Protein P10
1 entry
Infectivity protein P11
1 entry
Single-stranded DNA-binding protein (Protein P12)
1 entry
Protein P16 (GpS) (Protein S)
1 entry
Protein P17
1 entry
Protein P18 (GpM) (Protein M)
1 entry
Protein P19
1 entry
Minor capsid protein P30 (Protein P) (GpP)
1 entry
Penton protein P31 (GpC) (Protein C)
1 entry
Protein P32
1 entry
Protein P33
1 entry
Protein P34 (Protein O) (GpO)
1 entry
