Inhibition of host JAK1 by virus (kw:KW-1096)
JAK1 is widely expressed membrane-associated phosphoprotein involved in the interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction pathways. JAK1 and TYK2 participate in the interferon-alpha/beta pathway, while JAK1 and JAK2 play a role in the interferon-gamma pathway.
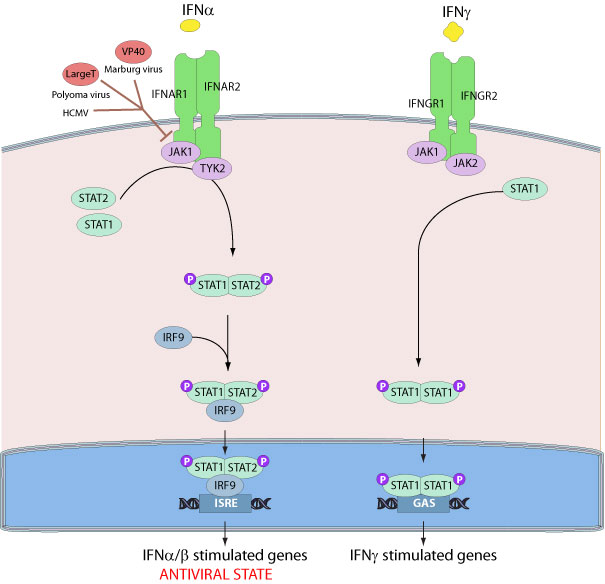
Several viruses have evolved specific mechanisms to prevent the establishment of an antiviral state by inhibiting key components of the signaling pathway. For instance, the polyomavirus large T antigen binds to Janus tyrosine kinase 1 and inactivated signaling through IFN receptors. The Marburg virus VP40 protein is able to prevent the tyrosine phosphorylation of JAK1 and subsequent phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT2.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)31 entries grouped by protein
3 entries
Protein MGF 505-7R
20 entries
Large T antigen (LT) (LT-AG) (EC 5.6.2.4) (DNA 3'-5' helicase large T antigen)
3 entries
Genome polyprotein
5 entries
