Asparagine proteases

Enzymatic reaction:
Enzymatic reaction:
- Asn-endopeptidase
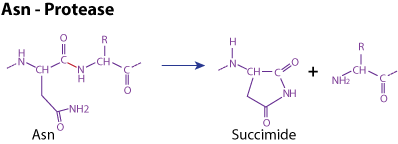
Mechanism The active site consists of an asparagine and at least one acidic amino acid (Asp, Glu). The terminal asparagine azote acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl atom of the peptide bond, forming a succimide residue and cleaving the peptide bond; the acidic amino acid assists the process by stabilizing the reaction intermediates.
| Genome | Order | Family | Function | Type | MEROPS family | Distribution (low incidence) | Clan (fold) | Interpro | UniProt exemplar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dsRNA | Nodamuvirales |   Nodaviridae Nodaviridae |
Self-cleavage, Virion maturation | Asparagine (Asn/Ala) | Peptidase N1 | Virus | NA | IPR000696 | Capsid protein precursor |
| ssRNA+ | Hepevirales |  Alphatetraviridae Alphatetraviridae |
Self-cleavage, Virion maturation | Asparagine (Asn/?) | Peptidase N2 | Virus | NA | IPR005313 | Capsid protein precursor |
| ssRNA+ | Durnavirales | Picobirnaviridae | Self-cleavage, Virion maturation | Asparagine | Peptidase N5 | Virus | NE | Capsid protein precursor | |
| dsRNA | Reovirales |   Spinareoviridae, Orthoreovirus, Aquareovirus Spinareoviridae, Orthoreovirus, Aquareovirus |
Self-cleavage, Virion maturation | Asparagine | Peptidase N7 | Virus | NC | IPR009113 | Outer capsid protein mu-1 |
| ssRNA+ | Picornavirales |   Picornaviridae, Enterovirus Picornaviridae, Enterovirus |
Self-cleavage, Virion maturation | Asparagine | Peptidase N8 | Virus | NA | IPR029053 | Polyprotein |
| ssRNA+ | Imitervirales |  Mimiviridae Mimiviridae |
Self-cleavage, Intein | Asparagine | Peptidase N10 | Animal, plant, protozoa, bacteria, archaea, virus | PD | IPR006141 | DNA polymerase |
| ssRNA+ | Algavirales |  Phycodnaviridae Phycodnaviridae |
Self-cleavage, Intein | Asparagine | Peptidase N10 | Animal, plant, protozoa, bacteria, archaea, virus | PD | IPR006141 | DNA polymerase |
Asparagine peptide lyases: a seventh catalytic type of proteolytic enzymes
Neil David Rawlings, Alan John Barrett, Alex Bateman
J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 4;286(44):38321-38328
Origins of peptidases
Neil D Rawlings, Alex Bateman
Biochimie. 2019 Nov;166:4-18.
