Polyomaviridae (taxid:151341)
VIRION
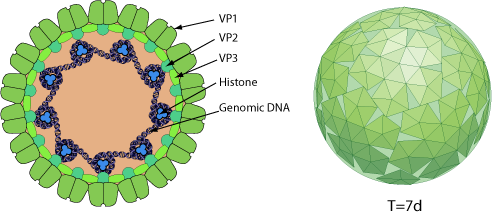
Non-enveloped capsid with a T=7d icosahedral symmetry, about 50 nm in diameter.
GENOME
Circular dsDNA about 5 kb in size, associated with cellular histones in a chromatin-like complex. Encodes for 5-9 proteins. On rare non-specific recombination, the viral genome can be integrated in host chromosome. This inactivates the integrated virus but can give the host cell a replicative advantage sometimes leading to malignant tumours.
GENE EXPRESSION
Transcription is nuclear, in two phases; early (replication), late (virion assembly/exit). 5-9 proteins are expressed from the two pre-MRNA by alternative splicing. All genes are transcribed by host RNA pol II.
REPLICATION
NUCLEAR
- Attachement of the viral proteins to host receptors triggers lipid-mediated endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Virion transits through endoplasmic reticulum where host protein disulfide isomerases rearrange its capsid structure
- Export of misfolded virion to the cytoplasm possibly through host ERAD pathway
- Loss of VP1 in the low-calcium conditions of the cytosol
- Import of genomic DNA into host nucleus.
- Transcription of early genes (LT and sT genes)
- Replication of the DNA genome in the nucleus.
- Transcription of late genes encoding for structural proteins (VP1, VP2 and VP3).
- Assembly of new virions in nuclear viral factories.
- Virions are released by lysis of the cell.
Host-virus interaction
Cell-cycle modulation
The large T antigen binds to host key cell cycle regulators retinoblastoma protein RB1/pRb and TP53 and induces the disassembly of host E2F1 transcription factors from RB1, thus promoting transcriptional activation of E2F1-regulated S-phase genes.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)91 entries grouped by protein
7 entries
Agnoprotein (Agno)
1 entry
Avian agnoprotein 1a (Agno-1a)
1 entry
Avian agnoprotein 2b (Agno-2b)
20 entries
Large T antigen (LT) (LT-AG) (EC 5.6.2.4) (DNA 3'-5' helicase large T antigen)
6 entries
Middle T antigen (MT) (MT-AG)
1 entry
SV40 early leader protein (SELP)
18 entries
Small t antigen (ST) (ST-AG)
19 entries
Major capsid protein VP1 (Major structural protein VP1)
18 entries
Minor capsid protein VP2 (Minor structural protein VP2)
Adelie penguin polyomavirus taxid:1590650
African elephant polyomavirus 1 taxid:1399914
Alphapolyomavirus apaniscus taxid:1236391
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14775 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21185 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-29844 |
| Small T antigen | ma-jd-viral-16548 |
Alphapolyomavirus chlopygerythrus taxid:1891719
Alphapolyomavirus molossi taxid:1606504
Alphapolyomavirus quartipanos taxid:1891736
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14785 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21121 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-29757 |
| Small T antigen | ma-jd-viral-16567 |
Alphapolyomavirus quintipanos taxid:1891737
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14761 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21214 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-29808 |
| Small T antigen | ma-jd-viral-16576 |
Alphapolyomavirus septipanos taxid:1891739
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14712 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21178 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-31166 |
| Small T antigen | ma-jd-viral-16628 |
Alphapolyomavirus sextipanos taxid:1891738
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14705 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21119 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-31161 |
| Small T antigen | ma-jd-viral-16645 |
Alphapolyomavirus tertichlopygerythrus taxid:1891720
Alphapolyomavirus tertipanos taxid:1891735
BK polyomavirus taxid:1891762
Bank vole polyomavirus taxid:1737522
Bat polyomavirus 5a taxid:1623687
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14735 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21140 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-29843 |
| Small t antigen | ma-jd-viral-16632 |
Bat polyomavirus 6a taxid:1623685
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14724 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21152 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-31177 |
| Small t antigen | ma-jd-viral-16540 |
Bat polyomavirus 6b taxid:1623689
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14711 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21112 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-31138 |
| Small t antigen | ma-jd-viral-16577 |
Bat polyomavirus 6c taxid:1623688
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14741 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21195 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-31176 |
| Small t antigen | ma-jd-viral-16572 |
Bat polyomavirus 6d taxid:1623686
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14779 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21210 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-31149 |
| Small t antigen | ma-jd-viral-16591 |
Betapolyomavirus calbifrons taxid:1236392
Betapolyomavirus cercopitheci taxid:1236395
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Agnoprotein | ma-jd-viral-59846 |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14797 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21107 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-29840 |
| Small t antigen | ma-jd-viral-16538 |
Betapolyomavirus equi taxid:1891761
Betapolyomavirus lepweddellii taxid:1925019
Betapolyomavirus mafricanus taxid:1891769
Betapolyomavirus mastomysis taxid:1891768
Betapolyomavirus ptedavyi taxid:1891773
Betapolyomavirus secuchlopygerythrus taxid:1891758
Betapolyomavirus securanorvegicus taxid:1919247
Betapolyomavirus tertihominis taxid:1891764
Black sea bass polyomavirus 1 taxid:1572341
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21223 |
| SLT | ma-jd-viral-21225 |
| SVP1 | ma-jd-viral-14691 |
| VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14690 |
| VP2 | ma-jd-viral-38176 |
Bornean orang-utan polyomavirus taxid:1604874
Butcherbird polyomavirus taxid:1394033
California sea lion polyomavirus 1 taxid:715223
Canary polyomavirus taxid:881945
Chaerephon polyomavirus 1 taxid:1276181
Chimpanzee polyomavirus Bob taxid:2035845
Common vole polyomavirus taxid:1737523
Gammapolyomavirus corvi taxid:1891748
Gammapolyomavirus pypyrrhula taxid:1891751
Gorilla gorilla gorilla polyomavirus 1 taxid:928214
Hamster polyomavirus taxid:1891729
Human polyomavirus 6 taxid:746830
Human polyomavirus 7 taxid:746831
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21163 |
| Small T antigen | ma-jd-viral-16597 |
| VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14771 |
| VP2 | ma-jd-viral-37806 |
| VP3 | ma-jd-viral-38147 |
Human polyomavirus 9 taxid:943908
JC polyomavirus taxid:10632
MW polyomavirus taxid:1203539
Macaca fascicularis polyomavirus 1 taxid:1236398
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14725 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21115 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-31140 |
| Small T antigen | ma-jd-viral-16583 |
Marbled eel polyomavirus taxid:1662286
Meles meles polyomavirus 1 taxid:1608323
Merkel cell polyomavirus taxid:493803
Murine polyomavirus (strain BG) taxid:179241
New Jersey polyomavirus-2013 taxid:1497391
Otomops polyomavirus KY156 taxid:2035998
Otomops polyomavirus KY157 taxid:2035999
Pan troglodytes troglodytes polyomavirus 1 taxid:1236400
Pan troglodytes verus polyomavirus 1a taxid:928211
Pan troglodytes verus polyomavirus 8 taxid:1762023
Piliocolobus rufomitratus polyomavirus 1 taxid:1236407
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21207 |
| Minor capsid protein VP2 (Minor structural protein VP2) | ma-jd-viral-48367 |
| Small T antigen | ma-jd-viral-16616 |
| VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14784 |
Polyomavirus sp. taxid:36362
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Capsid protein VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14716 |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21150 |
| Minor capsid protein | ma-jd-viral-31148 |
| Small T antigen | ma-jd-viral-16558 |
Raccoon polyomavirus taxid:1219896
Rattus norvegicus polyomavirus 1 taxid:1679933
STL polyomavirus taxid:1277649
Sea otter polyomavirus 1 taxid:1552409
Sheep polyomavirus 1 taxid:1634381
Sparus aurata polyomavirus 1 taxid:1885927
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Large T antigen | ma-jd-viral-21224 |
| ORF1 | ma-jd-viral-31901 |
| ORF2 | ma-jd-viral-67381 |
| VP1 | ma-jd-viral-14693 |
| VP2 | ma-jd-viral-40078 |
