Viral budding (kw:KW-1198)
Nucleocapsids assembled or in the process of being built induce formation of a membrane curvature in the host cell membrane and wrap up in the forming bud which is eventually pinched off by membrane scission to release the enveloped particle
 .
.
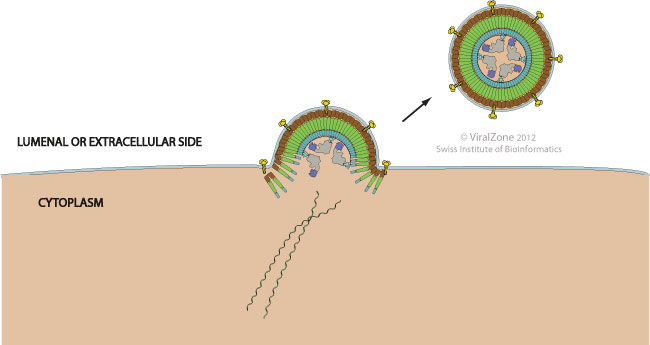
Many viruses, such as arena-, filo-, flavi-, hepadna-, herpes-, rhabdo-, and some paramyxoviruses, recruit host ESCRT proteins for budding.
However, for orthomyxo-, toga-, and corona- the budding is ESCRT-independent
 .
.
The only prokaryotic viruses known to bud are the Plasmaviridae
 .
.
Cell defense:
Tetherin expression that follows the establishment of the cell antiviral state impairs the release of many enveloped viruses
 .
.
ISG15 expression that follows the establishment of the cell antiviral state inhibits ESCRT-mediated viral budding. ISG15 is conjugated to CHMP5 and thereby disrupts further protein associations needed for functional ESCRT complex association
 .
.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)212 entries grouped by protein
121 entries
Gag polyprotein (Pr55Gag)
1 entry
P47(GAG-CRK) protein
44 entries
Matrix protein (Phosphoprotein M2)
5 entries
Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein)
7 entries
Envelope phospholipase OPG057 (EC 3.1.1.-) (EC 3.1.4.4) (37 kDa protein) (Envelope phospholipase F13) (Envelope protein F13) (Palmitoylated EV membrane protein) (p37K)
2 entries
Gag-Pro-Pol polyprotein
2 entries
Gag-Pro polyprotein
11 entries
Matrix protein VP40 (Ebola VP40) (eVP40) (Membrane-associated protein VP40)
19 entries
