Sedoreoviridae (taxid:2946186)
VIRION
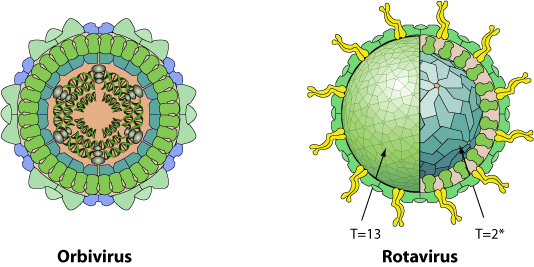
Non enveloped, icosahedral virion with a double capsid structure (except for cypoviruses and dinovernaviruses which have only the equivalent of the inner capsid). The outer capsid has a T=13 icosahedral symmetry, the inner capsid a T=2* icosahedral symmetry.
GENOME
Segmented linear dsRNA genome. Contains 10 to 12 segments coding for 10 to 14 proteins. Segments size range from 0.2 to 3.0 kb. Genome total size range from 18.2 to 30.5 kb.
GENE EXPRESSION
The dsRNA genome is never completely uncoated to prevent activation of antiviral state by the cell in response to dsRNA. Viral polymerase synthesizes mRNA from each of the dsRNA segments. These mRNAs are translocated to the cell cytoplasm where they are translated.
Further proteins are produced by leaky scanning and protein processing.
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachement to host receptors probably mediates endocytosis of virus into host cell.
- Particles are partially uncoated in endolysosomes, but not entirely, and penetrate in the cytoplasm.
- Early transcription of the dsRNA genome by viral polymerase occurs inside this sub-viral particle (naked core), so that dsRNA is never exposed to the cytoplasm.
- Transcription from each of the dsRNA segments produces mRNA templates for translation.
- Viral proteins and genomic RNAs aggregates in cytoplasmic viral factories.
- (+)RNAs are encapsidated in a sub-viral particle, in which they are transcribed to give RNA (-) molecules with which they become base-paired to produce dsRNA genomes.
- The capsid is assembled on the sub-viral particle.
- Mature virions are released presumably following cell death and associated breakdown of host plasma membrane.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
Bluetongue virus mediates host cell apoptosis via caspases activaton (caspases-8, caspases-9, caspase-3, and caspase-7)  .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
Rotaviruses counteract many antiviral pathways in a strain-specific manner
 :
:
NSP1 protein induces the proteasome-dependent degradation of IRF3, IRF5, and IRF7 to prevent their induction of IFN

 .
.
NSP1 can also induce proteasome-dependent degradation of the ubiquitin ligase complex protein beta-TrCP, resulting in stabilization of IκB and repress NF-κB
 .
.
 .
.
Rotavirus can prevent STAT1 and STAT2 nuclear translocation
 .
.
BTV NS4 might also be responsible for counteracting the antiviral response of the host
 .
.
Host gene expression shutoff by virus
Rotavirus NSP3 protein evicts cytoplasmic poly(A) binding protein (PABP) from translation initiation complexes and thus "shuts off the translation of cellular polyadenylated mRNAs"":/by_protein/1579.
Inhibition of host poly(A)-binding protein by virus -> Host translation shutoff

 .
.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by protein
Banna virus (strain Indonesia/JKT-6423/1980) taxid:649604
Callinectes sapidus reovirus 1 taxid:1811230
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| RNA-directed RNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.48) | ma-jd-viral-44575 |
Changuinola virus taxid:40052
Chobar Gorge virus taxid:1679172
Fengkai orbivirus taxid:1692107
Homalodisca vitripennis reovirus taxid:411854
Micromonas pusilla reovirus (isolate Netherlands/2005) taxid:649596
Mobuck virus taxid:1408137
Rotavirus A taxid:28875
Rotavirus A (isolate RVA/Monkey/South Africa/SA11-H96/1958/G3P5B[2]) taxid:450149
Rotavirus B (isolate RVB/Human/China/ADRV/1982) taxid:10942
Rotavirus C taxid:36427
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Intermediate capsid protein VP6 | ma-jd-viral-50193 |
