Lentivirus (taxid:11646)
VIRION
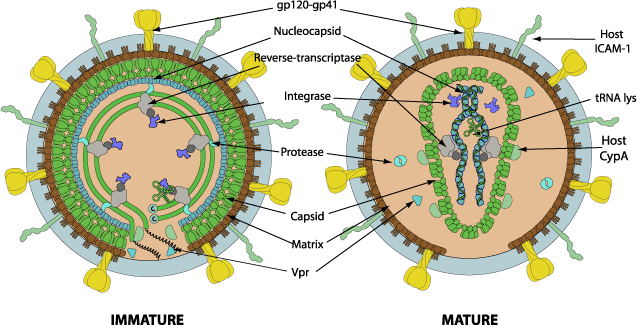
Enveloped, spherical to pleomorphic in shape, 80-100 nm in diameter. Mature capsid is quasi-icosahedral and contains 1572 capsid proteins.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, dimeric, ssRNA(+) genome of 9,75 kb, with a 5'-cap and a 3'poly-A tail. There are two long terminal repeats (LTRs) of about 600nt long at the 5' and 3' ends. The LTRs contain the U3, R, and U5 regions. There are also a primer binding site (PBS) at the 5'end and a polypurine tract (PPT) at the 3'end.
GENE EXPRESSION
The integrated provirus utilizes the promotor elements in the 5'LTR to drive transcription. This gives rise to the unspliced full length mRNA that will serve as genomic RNA to be packaged into virions or used as a template for translation of gag and gag-(pro)pol (1 ribosomal frameshift) polyproteins. The uncompletely spliced mRNAs encode env that is cleaved into SU and TM envelope proteins, and the accessory proteins vif, vpu, and vpr. Completely spliced mRNAs encode Rev, Tat and Nef accessory proteins. Rev escorts unspliced and uncompletely spliced RNAs out of the nucleus of infected cells.
ENZYMES
- Reverse transcriptase
- RNAse H [RT]
- Polyprotein protease (Peptidase A2) [PRO]
- Integrase [INT]
REPLICATION
NUCLEAR
Lytic replication:
- Virus attaches to host receptors through the SU glycoprotein (gp120), with subsequent interaction with a chemokine coreceptor. TM glycoprotein (gp41) mediates fusion with cell membrane.
- Internalization and partial uncoating.
- ssRNA(+) genome is copied into a linear dsDNA molecule by the reverse transcriptase.
- Nuclear entry of the viral dsDNA which is covalently and randomly integrated into the cell's genome by the viral integrase (=provirus).
- Transcription of provirus by Pol II produces viral spliced and unspliced RNAs.
- Translation of spliced viral RNAs produces tat, rev, and nef proteins.
- Rev mediates nuclear export of the uncompletely spliced RNAs.
- Translation of unspliced viral RNAs produces Env, Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins.
- Assembly of the virion at the host cellular membrane and packaging of the viral RNA genome.
- Budding through the plasma membrane and release of the virions.
- Proteolytic processing of the precursors polyproteins by viral protease and maturation of the virions.
Latent replication : replication as a provirus integrated in the host chromosome.
Host-virus interaction
Adaptive immune response inhibition
Lentiviruses have evolved different strategies to inhibit the host adaptive immune response. HIV-1 TAT acts at the transcriptional level by modifying proteasome composition by upregulating the LMP7 and MECL1 subunits and downregulating the LMP2 subunit, thereby promoting presentation of cryptic and subdominant CTL epitopes.
Three other HIV-1 proteins, Nef, Env and Vpu, contribute to downregulate CD4. Env forms a complex with CD4 in the endoplasmic reticulum, and retains the receptor in this compartment. Nef and Vpu target the receptor for degradation in the lysosome and the proteasome, respectively.
Apoptosis modulation
Vpr plays a role in the "induction of apoptosis" in HIV-1 infected cells via destabilization of the mitochondrial membrane leading to cytochrome C release and activation of the host caspase 9/3 pathway.
Autophagy modulation
HIV-1 Tat suppressed the induction of autophagy-associated genes and inhibited the formation of autophagosomes process  ,.
,.
Cell-cycle modulation
The Vpr protein form HIV-1 and HIV-2 induces a cell cycle arrest at G2/M transition through inactivation of the host cyclinB/cdc2 complex  .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
Tat can inhibit PKR activity by both RNA-dependent and RNA-independent mechanisms  .
.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)679 entries grouped by protein
101 entries
Envelope glycoprotein gp160 (Env polyprotein)
79 entries
Gag polyprotein (Pr55Gag)
69 entries
Protein Nef (3'ORF) (Negative factor) (F-protein)
1 entry
Uncharacterized ORF-X protein (Protein UPX)
75 entries
Gag-Pol polyprotein (Pr160Gag-Pol)
80 entries
Protein Rev (ART/TRS) (Anti-repression transactivator) (Regulator of expression of viral proteins)
70 entries
Protein Tat (Transactivating regulatory protein)
76 entries
Virion infectivity factor (Vif) (SOR protein)
59 entries
Protein Vpr (R ORF protein) (Viral protein R)
9 entries
Probable Vpr-like protein (Protein S) (Protein Tat)
35 entries
Protein Vpu (U ORF protein) (Viral protein U)
2 entries
Protein Vpw
21 entries
Protein Vpx (Viral protein X) (X ORF protein)
1 entry
Protein Vpy
1 entry
Uncharacterized protein ORF3 (ORFD)
Bovine immunodeficiency virus (strain R29) taxid:417296
Feline immunodeficiency virus (isolate Petaluma) taxid:11674
Human immunodeficiency virus 2 taxid:11709
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 taxid:11676
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Virion infectivity factor (Vif) (SOR protein) | ma-jd-viral-32085 |
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate BH10) taxid:11678
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Virion infectivity factor (Vif) (SOR protein) | ma-jd-viral-32085 |
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate BRU/LAI) taxid:11686
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Virion infectivity factor (Vif) (SOR protein) | ma-jd-viral-32085 |
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate HXB2) taxid:11706
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate PCV12) taxid:11679
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Virion infectivity factor (Vif) (SOR protein) | ma-jd-viral-32085 |
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 subtype A (isolate BEN) taxid:11714
Simian immunodeficiency virus taxid:11723
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Gag polyprotein | ma-jd-viral-67491 |
