Hepacivirus (taxid:11102)
VIRION
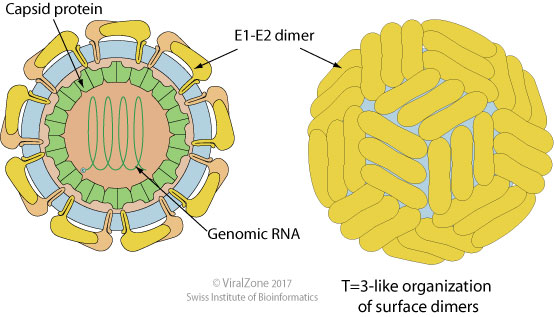
Enveloped, spherical, about 50 nm in diameter. Mature virions contain two virus-encoded membrane proteins (E1 and E2) in addition to the capsid protein.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, ssRNA(+) genome of about 10 kb. The genome 3' terminus is not polyadenylated but forms a loop structure. There is an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) at the 5' end that mediates translation initiation.
GENE EXPRESSION
The virion RNA is infectious and serves as both the genome and the viral messenger RNA. The whole genome is translated in a polyprotein, which is processed co- and post-translationally by host and viral proteases.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [NS5]
- FAD capping [NS5]
- Polyprotein major protease (Peptidase S29) [NS3]
- Self-cleavage N-ter polyprotein (Peptidase C18) [NS2]
REPLICATION
- Attachement of the viral envelope protein E to host receptors mediates internalization into the host cell by clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
- Fusion of virus membrane with host endosomal membrane. RNA genome is released into the cytoplasm.
- The positive-sense genomic ssRNA is translated into a polyprotein, which is cleaved into all structural and non structural proteins (to yield the replication proteins).
- Replication takes place at the surface of endoplasmic reticulum in cytoplasmic viral factories. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+). Host miRNA mir-122 plays a essential role in initiating replication.
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- Virus assembly occurs at the endoplasmic reticulum and seems to be facilitated by the viral ionic channel p7. The virion buds at the endoplasmic reticulum and is transported to the Golgi apparatus.
- Release of new virions by exocytosis.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
Flaviviruses NS3 induces apoptosis through host caspases activation

Autophagy modulation
Flaviviruses NS4A and NS4B induces autophagy signaling
 .
.
Cell-cycle modulation
Hepatitis C virus induces down-regulation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor and G1/S host cell cycle checkpoint dysregulation
 .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
Hepatitis C virus inhibits the interferon signaling pathway by blocking the IFN receptors  , STAT1 and TYK2
, STAT1 and TYK2
 .
.
Hepatitis C virus inhibits the host IFN-mediated response by blocking host MAVS  , TRAFs
, TRAFs  and TBK1-IKBKE-DDX3 complex
and TBK1-IKBKE-DDX3 complex  .
.
Host gene expression shutoff by virus
Hepatitis C virus activates PKR about 12h p.i. to shutoff host translation through the PKR-mediated phosphorylation of the eIF2alpha initiation factor  .
.
| IsolateID | Species | ICTV_ID | Exemplar or Additional | Virus name | Acronym | Isolate | Genome coverage | host | GenBankAC | UniProtAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VMR1009042 | Hepacivirus bovis | ICTV20165295 | E | bovine hepacivirus | BoHV | GER/2014 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | KP641127 | A0A0F7JH93 |
| VMR1009043 | Hepacivirus colobi | ICTV20165285 | E | guereza hepacivirus | GHV | 1/BWC08 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | KC551800 | S5E367 |
| VMR1009044 | Hepacivirus equi | ICTV20165283 | E | non-primate hepacivirus | NPHV | NZP1 | Complete genome | vertebrates | KP325401 | A0A0B5HK21 |
| VMR1009045 | Hepacivirus glareoli | ICTV20165291 | E | rodent hepacivirus | RHV-J | 3382/GER/2010 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | KC411777 | R9QTE4 |
| VMR1009046 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | E | hepatitis C virus genotype 1a | HCV1a | H77 | Complete genome | vertebrates | AF009606 | P27958 |
| VMR1012771 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 1a | HCV1a | PT | Complete genome | vertebrates | M62321 | P26664 |
| VMR1012772 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 1b | HCV1b | J | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | D90208 | P26662 |
| VMR1012773 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 2a | HCV2a | HC-J6 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | D00944 | P26660 |
| VMR1012774 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 2b | HCV2b | HC-J8 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | D10988 | P26661 |
| VMR1012775 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 3a | HCV3a | NZL1 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | D17763 | Q81258 |
| VMR1012776 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 3k | HCV3k | JK049 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | D63821 | Q68801 |
| VMR1012777 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 4a | HCV4a | ED43 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | GU814265 | D6P446 |
| VMR1012778 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 5a | HCV5a | EUH1480 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | Y13184 | O39928 |
| VMR1012779 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 6a | HCV6a | euhk2 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | Y12083 | O39927 |
| VMR1012780 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 6g | HCV6g | JK046 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | D63822 | Q68798 |
| VMR1012781 | Hepacivirus hominis | ICTV19910774 | A | hepatitis C virus genotype 7a | HCV7a | QC69 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | EF108306 | A8QPD9 |
| VMR1009047 | Hepacivirus macronycteridis | ICTV20165292 | E | bat hepacivirus | BHV-K | PDB-829 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | KC796074 | M9ZZL8 |
| VMR1009048 | Hepacivirus myodae | ICTV20165287 | E | rodent hepacivirus | RHV-F | 25842 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | KC411784 | R9QTQ6 |
| VMR1009049 | Hepacivirus norvegici | ICTV20165289 | E | Norway rat hepacivirus 2 | NRHV2 | E43 | Complete genome | vertebrates | KJ950939 | A0A097NZB6 |
| VMR1009050 | Hepacivirus otomopis | ICTV20165294 | E | bat hepacivirus | BHV-M | PDB-491.1 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | KC796078 | N0A109 |
| VMR1009051 | Hepacivirus peromysci | ICTV20165286 | E | rodent hepacivirus | RHV-E | 339 | Complete genome | vertebrates | KC815310 | M9UVS3 |
| VMR1009052 | Hepacivirus platyrrhini | ICTV20165284 | E | GB virus-B | GBV-B | B | Complete genome | vertebrates | U22304 | Q69422 |
| VMR1009053 | Hepacivirus ratti | ICTV20165288 | E | Norway rat hepacivirus 1 | NRHV1 | C12 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | KJ950938 | A0A097NZA3 |
| VMR1012782 | Hepacivirus ratti | ICTV20165288 | A | Norway rat hepacivirus 1 | NRHV1 | rn-1 | Complete genome | vertebrates | KX905133 | A0A247ZNN0 |
| VMR1009054 | Hepacivirus rhabdomysis | ICTV20165290 | E | rodent hepacivirus | RHV-I | 3/RSA/2008 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | KC411806 | R9QT72 |
| VMR1009055 | Hepacivirus vittatae | ICTV20165293 | E | bat hepacivirus | BHV-L | PDB-112 | Coding-complete genome | vertebrates | KC796077 | M9ZRW5 |
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by protein
