Degradation of host peptidoglycans during virus entry (kw:KW-1236)
Exolysin are viral lytic enzymes allowing digestion of bacterial cell wall upon virus entry. This activity is necessary for the virus to reach the host plasma membrane and inject its DNA in the host cytoplasm. The degradation is local, the virion drills a hole large enough to have its tail or capsid pass the wall.
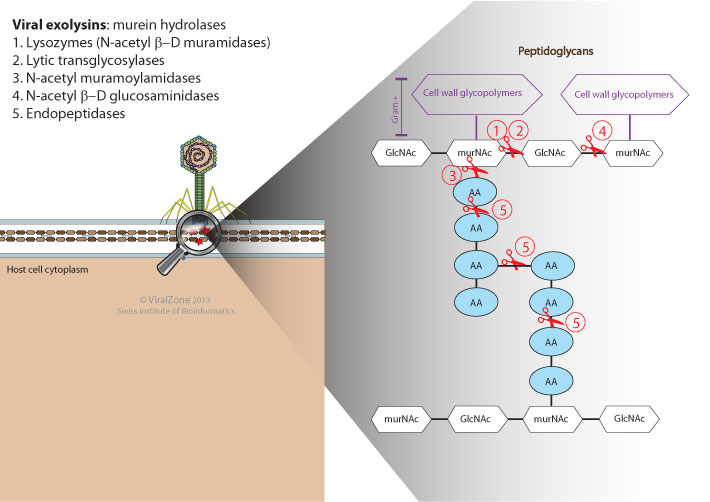
Depending on the enzymatic specificity, exolysins are divided into five main classes.
| Virus | family | Host bacteria | phage enzyme | ref. |
| Phage GA-1 | Podoviridae | Bacillus G1R | gp3 |  |
| Phage SPβ | Siphoviridae | Bacillus subtilis | YomI |  |
| Phage SPO1 | Myoviridae | Bacillus subtilis | - |  |
| Phage SPP1 | Siphoviridae | Bacillus subtilis | - |  |
| Phage M2 | Podoviridae | Bacillus subtilis | gp3 |  |
| Phage φ29 | Podoviridae | Bacillus subtilis | gp3 |  |
| Phage PRD1 | Tectiviridae | Escherichia coli | p7 |  |
| Phage T3 | Podoviridae | Escherichia coli | gp16 |  |
| Phage K1-5 | Podoviridae | Escherichia coli | orf35 |  |
| Phage N4 | Podoviridae | Escherichia coli | - |  |
| Phage T4 | Podoviridae | Escherichia coli | gp5 |  |
| Phage T5 | Siphoviridae | Escherichia coli | Pb2 |  |
| Phage C1 | Podoviridae | Escherichia coli | - |  |
| Phage φ949 | Unclassified | Lactococcus lactis | - |  |
| Phage φ31 | Siphoviridae | Lactococcus lactis | - |  |
| Phage φc2 | Myoviridae | Lactococcus lactis | - |  |
| Phage φr1t | Unclassified | Lactococcus lactis | - |  |
| Phage φ6 | Cystoviridae | Pseudomonas syringae | P5 |  |
| Phage φ13 | Cystoviridae | Pseudomonas syringae | - |  |
| Phage SP6 | Podoviridae | Salmonella typhimurium | orf35 |  |
| Phage φP22 | Podoviridae | Salmonella typhimurium | gp4 |  |
| Phage φYeO3-12 | Podoviridae | Yersinia enterocolitica | gp16 |  |
| Phage φKMV | Podoviridae | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | gp36 |  |
| Phage φKZ | Myoviridae | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | gp181 |   |
| Phage T7 | Podoviridae | Escherichia coli | gp16 |  |
Peptidoglycan hydrolytic activities associated with bacteriophage virions
Michael Moak, Ian J Molineux
Mol. Microbiol. February 2004; 51: 1169-1183
Michael Moak, Ian J Molineux
Mol. Microbiol. February 2004; 51: 1169-1183
Bacteriophage virion-associated peptidoglycan hydrolases: potential new enzybiotics
Lorena Rodriguez-Rubio, Beatriz Martinez, David M Donovan, Ana Rodriguez, Pilar Garcia
Crit. Rev. Microbiol. November 2013; 39: 427-434
Lorena Rodriguez-Rubio, Beatriz Martinez, David M Donovan, Ana Rodriguez, Pilar Garcia
Crit. Rev. Microbiol. November 2013; 39: 427-434
The structural peptidoglycan hydrolase gp181 of bacteriophage phiKZ
Yves Briers, Konstantin Miroshnikov, Oleg Chertkov, Alexei Nekrasov, Vadim Mesyanzhinov, Guido Volckaert, Rob Lavigne
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. October 3, 2008; 374: 747-751
Yves Briers, Konstantin Miroshnikov, Oleg Chertkov, Alexei Nekrasov, Vadim Mesyanzhinov, Guido Volckaert, Rob Lavigne
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. October 3, 2008; 374: 747-751
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)18 entries grouped by protein
9 entries
Head-to-tail adapter gp4 (Gene product 4) (Gp4) (Internal virion protein gp4) (Peptidoglycan hydrolase gp4)
2 entries
Morphogenesis protein 1 (Gene product 13) (gp13) (Protein p13)
1 entry
Pre-baseplate central spike protein Gp5 (Pre-Gp5) (Peptidoglycan hydrolase gp5) (EC 3.2.1.17)
4 entries
DNA terminal protein (Gene product 3) (gp3) (Protein p3)
2 entries
