Emaravirus (taxid:675845)
VIRION
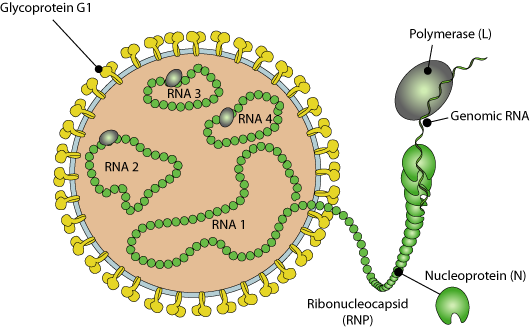
Enveloped, spherical.
GENOME
The genome is segmented and consists of four segments of linear negative-sense and single-stranded RNA. The complete genome is around 12.2 kb.
GENE EXPRESSION
The viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase (L) binds to a promoter on each encapsidated segment, and transcribes the mRNAs. These are capped by L protein during synthesis using cap snatching
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
IN PLANT:CYTOPLASMIC
- Virus penetrates into the cell by effraction or plasmodesmata transport.
- Sequential transcription.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- The ribonucleocapsid can penetrate in neighboring plant cells through plasmodesmata transport
- Alternatively budding of particles occurs at the cell membrane, releasing new virions.
IN INSECT:CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachment of the viral G glycoproteins to host receptors.
- Fusion of virus membrane with the vesicle membrane; ribonucleocapsid is released into the cytoplasm.
- Sequential transcription.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- Budding of particles occurs at the cell membrane, releasing new virions.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)4 entries grouped by strain
4 entries
European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus (isolate Sorbus aucuparia) (EMARAV) reference strain
Emaravirus cajani taxid:1980429
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Movement protein | ma-jd-viral-27814 |
| Putative glycoprotein | ma-jd-viral-50287 |
| Putative nucleocapsid protein | ma-jd-viral-09330 |
| p5 | ma-jd-viral-66309 |
