Bacterial host gene expression shutoff by virus (kw:KW-1261)
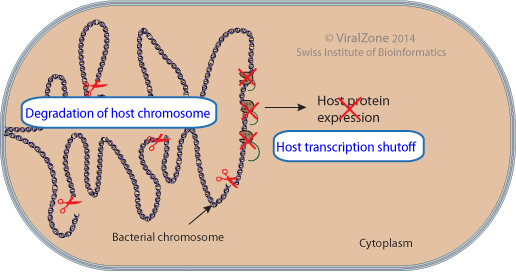
Bacterial viruses are in competition with the host for the cellular replication, transcription or translation machinery, prompting many of them to inhibit host cell gene expression. To achieve this goal, they possess a wide array of mechanisms that inactivate host transcription or even completely degrade the host chromosome.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)13 entries grouped by protein
1 entry
Protein A1
1 entry
Protein alc (Protein unf)
1 entry
DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease (EC 3.1.-.-) (AP endonuclease) (Apurinic-apyrimidinic endonuclease) (Protein 015)
1 entry
Endonuclease II (EC 3.1.21.8)
1 entry
Endonuclease I (EC 3.1.21.2) (Gene product 3) (Gp3) (Junction-resolving enzyme gp3)
2 entries
Exonuclease subunit 1 (EC 3.1.11.-) (Gene product 47) (gp47)
2 entries
Exonuclease subunit 2 (EC 3.1.11.-) (Gene product 46) (gp46)
1 entry
Exonuclease (Exonuclease gp6) (Gene product 6) (Gp6) (EC 3.1.11.3)
1 entry
Protein kinase 0.7 (EC 2.7.11.1) (Gene product 0.7) (Gp0.7) (Protein kinase gp0.7)
2 entries
