Arteriviridae (taxid:76803)
VIRION
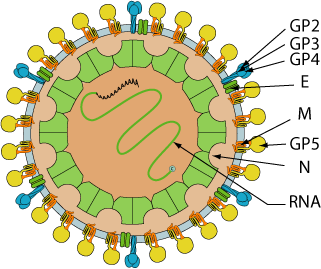
Enveloped, spherical, about 45-60 nm in diameter. The virion is comprised of an isometric core of 20-30 nm surrounded by a lipid-containing envelope. The RNA genome associates with the N protein to form the nucleocapsid.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear, ssRNA(+) genome of 12-16kb in size, capped, and polyadenylated. The leader RNA (65-89 bp) at the 5' end of the genome is also present at the end of each subgenomic RNAs.
GENE EXPRESSION
The virion RNA is infectious and serves as both genome and viral messenger RNA. ORF1b is translated by a ribosomal frameshifting. Polyproteins pp1a and pp1ab are processed into the viral polymerase (RdRp) and other non-structural proteins involved in RNA synthesis. Structural proteins are expressed as subgenomic RNAs. The mRNA2 is bicistronic. PRRSV, LDV and SHFV also express a truncated polyprotein 1aTF due to a ribosomal frameshifting in the nsp2 gene.
The 3' proximal region of SHFV contains in addition a large insertion that may encode three additional glycoproteins.
Protein GP2 and 5a are produced by leaky scanning from the E and gp5 subgenomic mRNA respectively.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [Q04561]
- Nido-type capping (GDP polyribonucleotidyltransferase, N7methyltransferase, 2'O methylase) [Q04561]
- EndoU ribonuclease [Q04561]
- Polyprotein major protease (Peptidase S32) [Q04561]
- Proteases (Peptidase C31, Peptidase C32, Peptidase C33) [Q04561]
- Helicase [Q04561]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachement to host receptors mediates clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- Fusion of virus membrane with the endosomal membrane. ssRNA(+) genome is released into the cytoplasm.
- Synthesis and proteolysis of replicase polyproteins.
- Replication occurs in viral factories. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+).
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- Synthesis of structural proteins encoded by subgenomic mRNAs.
- assembly and ESCRT-independent budding at the membranes of endoplasmic reticulum (ER), intermediate compartments, and/or Golgi complex.
- Release of new virions by exocytosis.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
The equine arteritis virus and PRRSV induce apoptosis via host caspases activation (caspase-8 and mitochondria-dependent caspase-9)


Autophagy modulation
PRRSV induces autophagy to promote virus replication


 .
.
Innate immune response inhibition
PRRSV clearly inhibits the type-I IFN response and down-regulates TLR3, TLR7, and TLR8 expression.
At least three non-structural proteins (Nsp1, Nsp2, and Nsp11) play roles in the IFN suppression and NF-κB pathways

 :
:
Nsp1α subunit inhibits the IκB phosphorylation in the cytoplasm and therefore the activation of NF-κB.
Nsp1β inhibits phosphorylation of STAT1 and nuclear translocation of ISGF3 complex (composed of STAT1, STAT2 and IRF9).
Nsp1β prevents IRF3 activation, thereby interfering with the RIG-I signaling pathway

 .
.
Nsp2 inhibits IFN production by blocking the ubiquitinylation of phosphorylated IκB and phosphorylation of IRF3 through the OTU domain. Nsp2 has the potential to deconjugate ISGylation.
Nsp11 suppresses IFN-β production through degradation of IPS-1 mRNA. For the second wave of IFN signaling, PRRSV Nsp1β blocks the phosphorylation of STATs and inhibits the nuclear translocation of ISGF3 complex (composed of STAT1, STAT2 and IRF9).
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)40 entries grouped by protein
1 entry
Truncated polyprotein 1aTF
3 entries
Envelope small membrane protein (Protein E) (Glycoprotein 2b) (Protein GP2b) (Gs)
2 entries
Glycoprotein 2a (Protein GP2a) (GP2)
1 entry
Glycoprotein 2b (Protein GP2b) (GP(S))
3 entries
Glycoprotein 3 (Protein GP3)
3 entries
Glycoprotein 4 (Protein GP4)
3 entries
Glycoprotein 5 (Protein GP5) (G(L))
3 entries
Membrane protein (Protein M)
5 entries
Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) (Protein N)
3 entries
Structural protein ORF5a
10 entries
Replicase polyprotein 1ab (ORF1ab polyprotein)
1 entry
Replicase polyprotein 1TF (ORF1ab polyprotein)
2 entries
