Holin/endolysin/spanin cell lysis
 .
.Two proteins, an endolysin and a holin are usually required for programmed host cell lysis by dsDNA prokaryotic viruses  . Additional proteins called spanins are involved in the lysis process in Gram-negative hosts. A multistep process allows a better control of lysis timing
. Additional proteins called spanins are involved in the lysis process in Gram-negative hosts. A multistep process allows a better control of lysis timing .
.
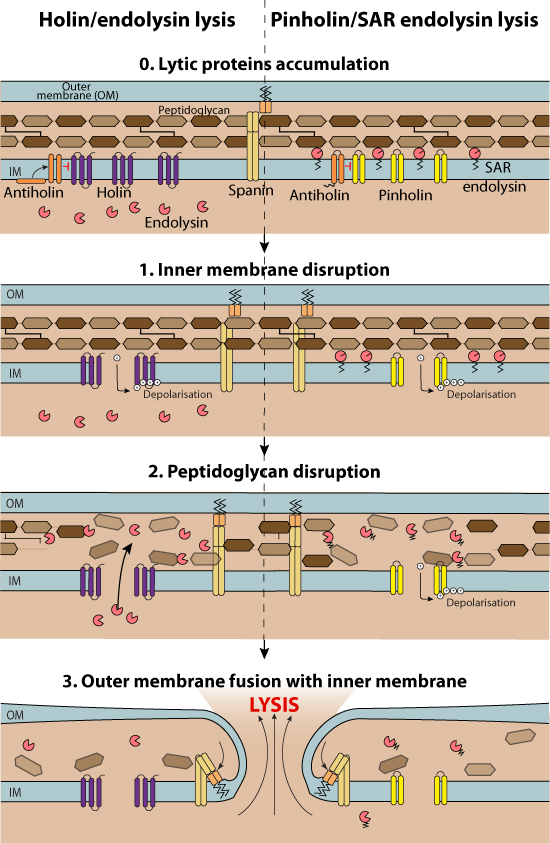
1. Cell membrane disruption (Gram-negative host, Gram-positive host)
Holins (from making "holes") are small membrane proteins that control the lysis timing. They accumulate in the host cell membrane until, at a programmed time (probably when reaching a critical concentration), they aggregate into oligomers and permeabilize the host cytoplasmic membrane inducing loss of polarization.
Canonical holins form large pores at one side of the bacteria, exposing locally the peptidoglycans to cytoplasmic canonical endolysin molecules 
 . The outcome of this kind of lysis is a localized envelope catastrophe: "local blow-out".
. The outcome of this kind of lysis is a localized envelope catastrophe: "local blow-out".
Pinholins form small pores that result in membrane depolarization, triggering SAR endolysin activation and degradation of peptidoglycans in the whole cellular periplasmic space. The outcome of this kind of lysis is a general lysis of the outer membrane of the host cell.
Antiholins associate specifically with the holins or pinholins giving rise to inactive heteromultimers. This allows a larger accumulation of holin molecules without any risk of premature aggregation before the triggering time.
ssDNA and ssRNA prokaryotic viruses usually have a "single gene lysis" which is thought to inhibit the peptidoglycan layer polymerization.
The advantage of the two-component system is that holins allow a abrupt and time-determined lysis thus preventing slow host cell deterioration.
2. Peptidoglycan disruption (Gram-negative host, Gram-positive host)
Endolysins are muralytic enzymes that degrade the host cell wall. Depending on the absence or presence of a signal sequence, endolysins are classified as canonical endolysins (no signal sequence) and signal-anchor-release endolysins (SAR endolysins, N-terminal type II signal anchor). Canonical endolysins accumulate in the cytoplasm and are released at a precise timing through the large holes generated by the aggregation of holin molecules.
SAR endolysins are already bound on the periplasmic side of the cell membrane and thus do not need to transit through large holes in the cell membrane. Instead, their release occurs through membrane depolarization performed by pinholins, which make small holes in the host cell membrane (about 2 nm in diameter)  .
.
3. Outer membrane disruption (Gram-negative host)
Spanins are essential for the lysis of bacteria with both internal (IM) and outer (OM) membranes (mostly Gram-negative). Lysis of these host bacteria additionally requires the disruption of the outer membrane. Spanins span the inner and outer membrane either as a unimolecular (u-spanin) or as a heterodimer molecule (IM-spanin or i-spanin + OM-spanin or o-spanin) 
 .
.
After cell wall degradation by the endolysin, the spanin complexes are free to diffuse and aggregate. the lytic blowout occurs when sufficient spanin complexes are liberated within the degraded area of the PG. They mediate the fusion of the IM and OM, thereby disrupting the cell membranes  .
.
Examples of lysis cassettes:
| Virus | Family | Genus | Phage lysis protein | Reference |
| Phage T4 | Myoviridae | T4likevirus | Endolysin |  Programmed Escherichia coli cell lysis by expression of cloned T4 phage lysis genes M Morita, K Asami, Y Tanji, H Unno Biotechnol. Prog. June 2001; 17: 573-576 |
| Holin |  Programmed Escherichia coli cell lysis by expression of cloned T4 phage lysis genes M Morita, K Asami, Y Tanji, H Unno Biotechnol. Prog. June 2001; 17: 573-576 |
|||
| Spanin, outer membrane subunit |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
|||
| Spanin, inner membrane subunit |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
|||
| Antiholin |  An ancient player unmasked: T4 rI encodes a t-specific antiholin E Ramanculov, R Young Mol. Microbiol. August 2001; 41: 575?583  Protein determinants of phage T4 lysis inhibition Samir H Moussa, Vladimir Kuznetsov, Tram Anh T Tran, James C Sacchettini, Ry Young Protein Sci. April 2012; 21: 571-582 |
|||
| Phage P2 | Myoviridae | P2likevirus | Endolysin |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
| Holin |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112  Functional analysis of a class I holin, P2 Y Kam H To, Jill Dewey, Jeremy Weaver, Taehyun Park, Ry Young J. Bacteriol. March 2013; 195: 1346-1355 |
|||
| Antiholin |  Functional analysis of a class I holin, P2 Y Kam H To, Jill Dewey, Jeremy Weaver, Taehyun Park, Ry Young J. Bacteriol. March 2013; 195: 1346-1355 |
|||
| Spanin, inner membrane subunit |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
|||
| Spanin, outer membrane subunit |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
|||
| Phage P22 | Podoviridae | P22likevirus | Endolysin |  Phage P22 lysis genes: nucleotide sequences and functional relationships with T4 and lambda genes D Rennell, A R Poteete Virology May 1985; 143: 280-289 |
| Holin |  Phage P22 lysis genes: nucleotide sequences and functional relationships with T4 and lambda genes D Rennell, A R Poteete Virology May 1985; 143: 280-289 |
|||
| Spanin, inner membrane subunit |  Nucleotide sequence of the bacteriophage P22 gene 19 to 3 region: identification of a new gene required for lysis S Casjens, K Eppler, R Parr, A R Poteete Virology August 1989; 171: 588?598 |
|||
| Spanin, outer membrane subunit | - | |||
| Phage φKMV | Podoviridae | Phikmvlikevirus | SAR endolysin |  The lysis cassette of bacteriophage φKMV encodes a signal-arrest-release endolysin and a pinholin Yves Briers, Liesbet M Peeters, Guido Volckaert, Rob Lavigne Bacteriophage 2011; 1: 25-30 |
| Pinholin |  The lysis cassette of bacteriophage φKMV encodes a signal-arrest-release endolysin and a pinholin Yves Briers, Liesbet M Peeters, Guido Volckaert, Rob Lavigne Bacteriophage 2011; 1: 25-30 |
|||
| Spanin, inner membrane subunit |  The lysis cassette of bacteriophage φKMV encodes a signal-arrest-release endolysin and a pinholin Yves Briers, Liesbet M Peeters, Guido Volckaert, Rob Lavigne Bacteriophage 2011; 1: 25-30 |
|||
| Spanin, outer membrane subunit |  The lysis cassette of bacteriophage φKMV encodes a signal-arrest-release endolysin and a pinholin Yves Briers, Liesbet M Peeters, Guido Volckaert, Rob Lavigne Bacteriophage 2011; 1: 25-30 |
|||
| Phage T7 | Podoviridae | T7likevirus | Holin |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
Spanin, inner membrane subunit |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
Spanin, outer membrane subunit |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
| Phage lambda | Siphoviridae | Lambdalikevirus | Endolysin |  Cell lysis by induction of cloned lambda lysis genes J Garrett, R Fusselman, J Hise, L Chiou, D Smith-Grillo, J Schulz, R Young Mol. Gen. Genet. 1981; 182: 326-331 |
| Holin |  Holin triggering in real time Rebecca White, Shinobu Chiba, Ting Pang, Jill S Dewey, Christos G Savva, Andreas Holzenburg, Kit Pogliano, Ry Young Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. January 11, 2011; 108: 798-803 |
|||
| Spanin, inner membrane subunit |  Spanin function requires subunit homodimerization through intermolecular disulfide bonds Joel D Berry, Manoj Rajaure, Ry Young Mol. Microbiol. April 2013; 88: 35-47 |
|||
| Spanin, outer membrane subunit |  Spanin function requires subunit homodimerization through intermolecular disulfide bonds Joel D Berry, Manoj Rajaure, Ry Young Mol. Microbiol. April 2013; 88: 35-47 |
|||
| Phage T1 | Siphoviridae | Tunalikevirus | Endolysin |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
Holin |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
u-Spanin |  Rz/Rz1 lysis gene equivalents in phages of Gram-negative hosts Elizabeth J Summer, Joel Berry, Tram Anh T Tran, Lili Niu, Douglas K Struck, Ry Young J. Mol. Biol. November 9, 2007; 373: 1098-1112 |
Ry Young
Curr. Opin. Microbiol. December 2013; 16: 790-797
I N Wang, D L Smith, R Young
Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000; 54: 799-825
Rebecca White, Shinobu Chiba, Ting Pang, Jill S Dewey, Christos G Savva, Andreas Holzenburg, Kit Pogliano, Ry Young
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. January 11, 2011; 108: 798-803
Ting Pang, Tinya C Fleming, Kit Pogliano, Ry Young
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. May 28, 2013; 110: E2054-2063
Joel Berry, Manoj Rajaure, Ting Pang, Ry Young
J. Bacteriol. October 2012; 194: 5667-5674
Joel D Berry, Manoj Rajaure, Ry Young
Mol. Microbiol. April 2013; 88: 35-47
Joel Berry, Manoj Rajaure, Ting Pang, Ry Young
J. Bacteriol. October 2012; 194: 5667-5674
Ryland Young
J. Microbiol. March 2014; 52: 243-258
Mart Krupovic, Rimantas Daugelavicius, Dennis H Bamford
Mol. Microbiol. June 2007; 64: 1635-1648
Yi Zheng, Douglas K Struck, Chelsey A Dankenbring, Ry Young
Microbiology (Reading, Engl.) June 2008; 154: 1710-1718
Manoj Rajaure, Joel Berry, Rohit Kongari, Jesse Cahill, Ry Young
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. April 28, 2015; 112: 5497?5502
