Tospoviridae (taxid:1980419)
VIRION
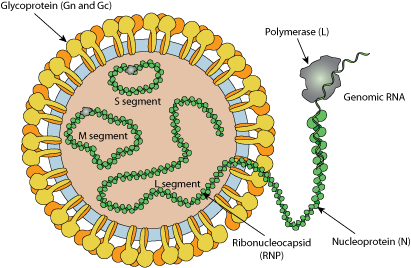
Enveloped, spherical. Diameter from 80 to 120nm.
GENOME
Segmented Negative-stranded RNA linear genome, L segment is about 8.8kb, M segment about 4.8kb and S segment about 3kb.
Encodes for six proteins.
GENE EXPRESSION
Transcription starts by viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase (L) binding to a promoter on each encapsidated segment, and is terminated by a strong hairpin sequence at the end of each gene. mRNAs are capped by L protein during synthesis using cap snatching , but are not polyadenylated.
S and M segments uses ambisense strategy to encode forsevral proteins: both genomic ans antigenomic RNA are transcribed. The hairpin sequence is a stop polymerase signal which prevents ambisense transcription from producing dsRNA. MRNA1 encodes for a polyprotein which is cleaved by host protease into Gn and Gc proteins.
ENZYMES
REPLICATION
IN PLANT:CYTOPLASMIC
- Virus penetrates into the cell by effraction or plasmodesmata transport.
- Cytoplasmic transcription by viral polymerase on the RNA viral RNA template.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- The ribonucleocapsid can penetrate in neighboring plant cells through plasmodesmata transport
- Alternatively budding of particles occurs at the cell membrane, releasing new virions.
IN INSECT:CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachment of the viral G glycoproteins to host receptors.
- Fusion of virus membrane with the vesicle membrane; ribonucleocapsid is released into the cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasmic transcription by viral polymerase on the RNA viral RNA template.
- Replication presumably starts when enough nucleoprotein is present to encapsidate neo-synthetized antigenomes and genomes.
- Budding of particles occurs at the cell membrane, releasing new virions.
Host-virus interaction
Inhibition of host innate immunity
TSWV NSs inhibits Dicer-mediated dsRNA processing thereby inhibiting RNAi-mediated immunity  to control innate immune signaling.
to control innate immune signaling.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)17 entries grouped by strain
5 entries
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain Brazilian Br-01) (TSWV) reference strain
4 entries
Impatiens necrotic spot virus (INSV)
2 entries
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain Bulgarian L3) (TSWV)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (isolate D) (TSWV)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain Brazilian Br-03) (TSWV) (Tomato chlorotic spot virus)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain Hawaiian) (TSWV)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain Regular2A) (TSWV)
1 entry
Tomato spotted wilt virus (strain SA-05) (TSWV) (Groundnut ringspot virus)
Bean necrotic mosaic virus taxid:1033976
Capsicum chlorosis virus taxid:163325
Chrysanthemum stem necrosis virus taxid:83871
Groundnut ringspot and Tomato chlorotic spot virus reassortant taxid:1027232
Melon yellow spot virus taxid:89471
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelopment polyprotein (M polyprotein) | ma-jd-viral-30770 |
| Nonstructural protein | ma-jd-viral-27544 |
Pepper chlorotic spot virus taxid:1414655
Tomato zonate spot virus taxid:460926
Tospovirus kiwifruit/YXW/2014 taxid:1857323
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Envelopment polyprotein (M polyprotein) | ma-jd-viral-30775 |
| NSs | ma-jd-viral-47179 |
| Nsm | ma-jd-viral-27530 |
| Nucleoprotein (Nucleocapsid protein) | ma-jd-viral-09325 |
