Picornaviridae (taxid:12058)
VIRION
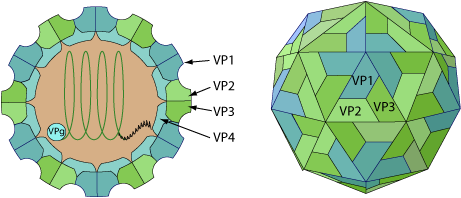
Non-enveloped, spherical, about 30 nm in diameter, pseudo T=3 icosahedral capsid surrounding the naked RNA genome. The capsid consists of a densely-packed icosahedral arrangement of 60 protomers, each consisting of 4 polypeptides, VP1, VP2, VP3 and VP4. VP4 is located on the internal side of the capsid.
GENOME
Monopartite, linear ssRNA(+) genome of 7.1-8.9 kb, polyadenylated, composed of a single ORF encoding a polyprotein. Viral genomic RNA has a viral protein (VPg) at its 5' end instead of a methylated nucleotide cap structure. The long UTR at the 5' end contains an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). The P1 region encodes the structural polypeptides. The P2 and P3 regions encode the nonstructural proteins associated with replication. The shorter 3' UTR is important in (-)strand synthesis. L is an additional N-terminal leader protein present in some genera that can either be a papain-like cysteine proteinases (genera aphthovirus, erbovirus) or have another function (genera kobuvirus, cardiovirus, teschovirus, sapelovirus, senecavirus). Enzymes:RNA dependent RNA polymerase, VPG Nucleotidylylase, terminal adenylyltransferase, proteases.
GENE EXPRESSION
The virion RNA is infectious and serves as both the genome and viral messenger RNA. The IRES allows direct translation of the polyprotein. The polyprotein is initially processed by the viral protease(s) into various precursor and mature proteins to yield the structural proteins, replicase, VPg, and a number of proteins that modify the host cell, ultimately leading to cell lysis.
ENZYMES
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [RdRp]
- VPG-type capping [VPg]
- NTPase-helicase [2C]
- Polyprotein major protease (Peptidase C3) [3Cpro, 2A]
- Self cleaving protease (Peptidase C28) [L]
REPLICATION
CYTOPLASMIC
- Attachement of the virus to host receptors mediates endocytosis of the virus into the host cell.
- The capsid undergoes a conformational change and releases VP4 that opens a pore in the host endosomal membrane and the viral genomic RNA penetrates into the host cell cytoplasm.
- VPg is removed from the viral RNA, which is then translated into a processed polyprotein.
- In entero-, rhino-, and aphthoviruses, shutoff of cellular cap-dependent translation through the cleavage of translation initiation factors by viral protease.
- Replication occurs in viral factories made of membrane vesicles derived from the ER. A dsRNA genome is synthesized from the genomic ssRNA(+).
- The dsRNA genome is transcribed/replicated thereby providing viral mRNAs/new ssRNA(+) genomes.
- New genomic RNA is believed to be packaged into preassembled procapsids.
- Cell lysis and virus release.
- Maturation of provirions by an unknown host protease.
Host-virus interaction
Apoptosis modulation
Picornaviruses modulate host apoptosis  .
.
Poliovirus infection activates the apoptotic pathway, involving mitochondrial damage, cytochrome c efflux, and consecutive activation of caspases (caspase-3 caspase and -9)  , whereas antiapoptotic activity has been attributed to cardiovirus leader protein
, whereas antiapoptotic activity has been attributed to cardiovirus leader protein  .
.
Modulation of apoptosis depends on the host cell-type and on the time the infection because of the presence of viral pro- and anti-apoptotic factors respectively at the beginning and at the end of the infectious cycle


 .
.
Autophagy modulation
Picornaviruses subvert the cell autophagic pathway to facilitates viral infection  :
:
- Human rhinovirus 2 and EMCV activates the autophagic pathway

- Foot-and-mouth disease virus utilizes the autophagic pathway

- Coxsackievirus and poliovirus infection induces autophagy-like vesicles


Innate immune response inhibition
Picornaviruses inhibit the host IFN-mediated response by inactivating either MDA-5, RIG-I, MAVS or IRF-3:
- HAV cleaves and inhibits MAVS 
- Coxsackievirus B3 cleaves and inhibits MAVS 
- Enteroviruses and cardiviruses cleave and inhibit RIG-I

-Poliovirus cleaves and inhibits MDA-5

- Mengovirus and foot-and-mouth disease virus leader proteins inhibit IRF-3

 .
.
Picornaviruses inhibit Toll-like receptor 3 mediated antiviral response as well:
- Coxsackievirus B 3C, HAV and enterovirus 71 proteases 3C cleave TRIF 

 .
.
Host gene expression shutoff by virus
Picornaviruses inhibit host translation by cleaving various translation factors such as PABP (FMDV, poliovirus and coxsackievirus) 
 , eIF3a, eIF3b (FMDV)
, eIF3a, eIF3b (FMDV)
 , eIF5B
, eIF5B  and activating 4E-BP1
and activating 4E-BP1  .
.
Poliovirus also inhibits host transcription by cleaving the TATA-binding protein  .
.
Some enteroviruses or cardioviruses inhibit host mRNA export as well.




Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)0 entry grouped by strain
hepatovirus B1 taxid:1708572
| Protein | ModelArchive |
| Genome polyprotein | ma-jd-viral-30863 |
