Viruses have evolved ways of suppressing host mRNAs expression to favor their survival and maximize expression of their own mRNAs. Decimating cellular mRNAs eventually leads to shutoff of host proteins expression and gives viruses transcripts a competitive edge for access to the cellular translation machinery.
Preventing the expression of host proteins is also a strategy to counteract the antiviral response.
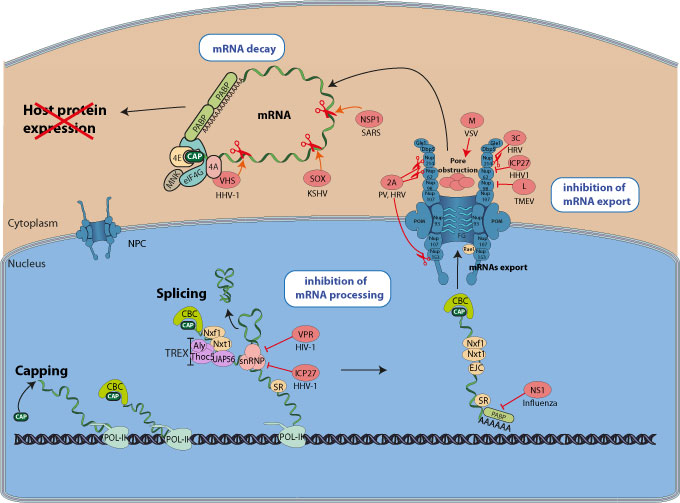
Some viruses interfere with host pre-mRNA processing function (splicing or polyadenylation), whereas other induce the host mRNAs degradation or block their export out of the nucleus.
Viruses inhibiting host mRNA splicing:
| Family | Virus | Viral protein | mRNA suppression strategy | references |
| Orthomyxoviridae | Influenza A virus | NS1 | Inhibition of polyadenylation & nuclear export |




|
| Herpesviridae | HHV1, HHV2 ( Simplexvirus) | ICP27 | Inhibition of splicing & nuclear export |




|
| VHS protein | mRNA decay |
  

|
HHV-8/KSHV ( Gammaherpesvirinae ) | SOX protein (ORF37) | mRNA decay |





|
| MHV68 ( Rhadinovirus ) | SOX protein | mRNA decay |

|
|
| EBV ( Lymphocryptovirus ) | BGLF5 | mRNA decay |

|
|
| Retroviridae | HIV-1 | VPR | Inhibition of splicing |

|
| Coronaviridae | SARS coronavirus | NSP1 | mRNA decay |

|
| Picornaviridae | Poliovirus ( Enterovirus ) | 2A protease | Inhibition of nuclear export |


|
| Theiler's virus ( Cardiovirus ) | Leader protein | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|
|
| EMCV ( Cardiovirus ) | Leader protein | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|
|
| HRV16 ( Enterovirus ) | 3C protease | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|
|
| HRV14 ( Enterovirus ) | ? | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|
|
| Rhabdoviridae | Vesicular stomatitis virus ( Vesiculovirus ) | M protein | Inhibition of nuclear export |


|
| Adenoviridae | Adenovirus ( Mastadenovirus ) | ? | Inhibition of nuclear export |

|

