Inhibition of host interferon receptors by virus (kw:KW-1091)
Type I interferons play an essential role in maintaining a defense against viral infection. These cytokines also participate in the control of cell proliferation. These effects are triggered by ligand binding to a specific cell surface receptor. IFN receptors (IFN-R) are composed of two chains, α and β, and transduce signals via the classical Jak-Stat pathway.
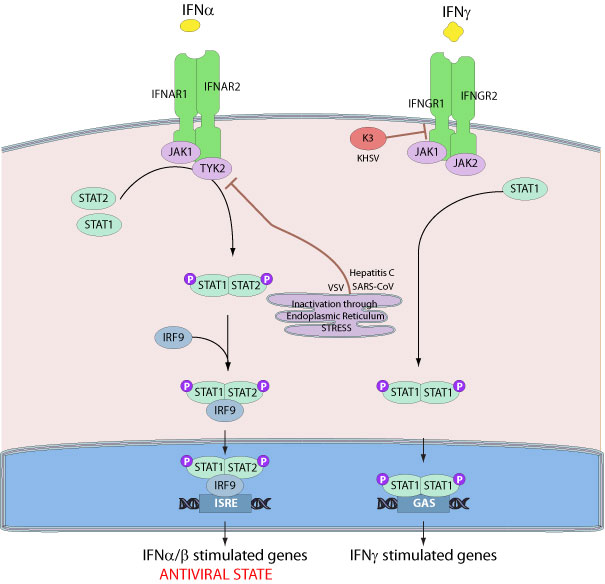
Several viruses induce the ER stress response also named the unfolded protein response (UPR). Such activation requires the endoplasmic reticulum resident protein kinase PERK. The activation of this pathway promotes phosphorylation- dependent ubiquitination and degradation of IFNAR1, specifically inhibiting type I IFN signaling and antiviral defenses.
Matching UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries
(all links/actions below point to uniprot.org website)3 entries grouped by strain
2 entries
Human herpesvirus 8 type P (isolate GK18) (HHV-8) (Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus) reference strain
1 entry
